Swiss tech tree for World of Tanks proposal by PikPikker
- AP/AP
- 40/40 HP
- 74/90 mm
- 10
- 0.3 s
- 22 s
- AP/AP
- 50/50 HP
- 105/140 mm
- 10
- 0.3 s
- 22 s
- 380 m
- 415 m
- 680 m
- 65 hp
- 85 hp
- 110 hp
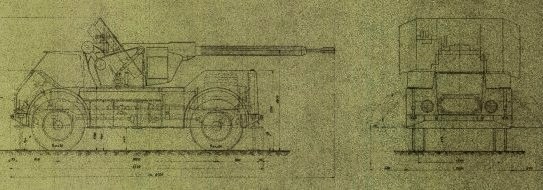
Вариант вооружения самого массового швейцарского грузовика Saurer CR 1 D зенитным 34-мм орудием конструкции Адольфа Фурера. Отличительной черта данного орудия - высокий темп стрельбы. Машина не покинула стадии чертежей.

* - only in front section; -5/45 the rest.

- AP/AP/HE
- 150/150/200 HP
- 100/123/20 mm
- AP/AP/HE
- 180/180/240 HP
- 126/151/34 mm
- AP/AP/HE
- 180/180/240 HP
- 173/206/34 mm
- 415 m
- 680 m
- 104 hp
- 160 hp
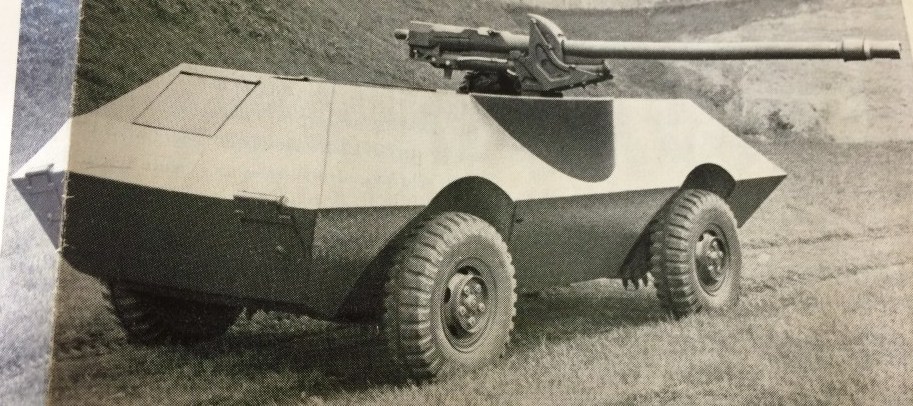

Во второй половине 1950-х MOWAG предложила несколько различных вариантов вооружения БТР MR-8 Wotan. Один из них предполагал установку 75-мм орудия. Проект не покинул стадии макета.


- AP/AP/HE
- 180/180/240 HP
- 126/151/34 mm
- AP/HEAT/HE
- 240/240/320 HP
- 165/210/45 mm
- 12/12 mm
- 20/12 mm
- 415 m
- 680 m
- 760 m
- 104 hp
- 160 hp

Во второй половине 1950-х MOWAG предложила несколько различных вариантов вооружения БТР MR-8 Wotan. Один из них предполагал установку 90-мм орудия. Проект не покинул стадии макета.


- AP/HEAT/HE
- 240/240/320 HP
- 165/205/45 mm
- AP/AP/HE
- 240/240/320 HP
- 205/290/45 mm
- 12/12/12 mm
- 20/12/12 mm
- 680 m
- 760 m
- 104 hp
- 160 hp
Во второй половине 1950-х MOWAG предложила несколько различных вариантов вооружения БТР MR-8 Wotan. Один из них предполагал установку 90-мм орудия. Проект не покинул стадии макета.


- AP/AP/HE
- 240/240/320 HP
- 205/290/45 mm
- HEAT/HEAT/HE
- 320/320/400 HP
- 240/305/85 mm
- 40/20 mm
- 680 m
- 760 m
- 140 hp
- 200 hp
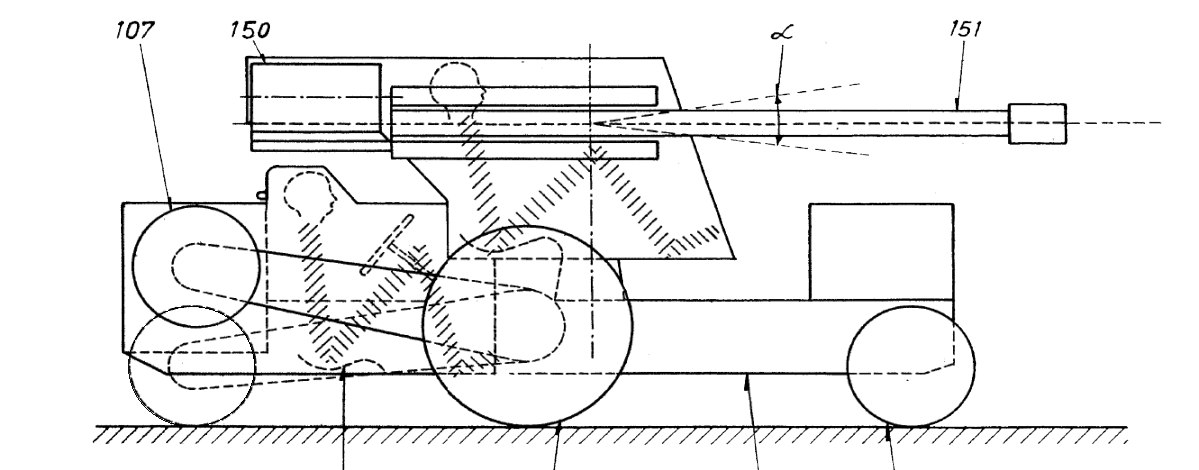
После войны фирма Meili разработала прототип грузовика Meili Flextruck, предназначенного для использования в гористой местности. Грузовик имел сочлененный корпус, позволявший преодолевать препятствия и давший машине лучшую проходимость. В надежде, что такую разработку можно применить в военном деле, был представлен аванпроект истребителя танков. Отличительными чертами проекта, среди прочего, были крайне компактные габариты и отличная проходимость (благодаря сочлененному корпусу). Кроме того, была проработана возможность использования надеваемых гусеничных лент, как на танках БТ. Однако ввиду своей дороговизны, проект был отклонён.
New propulsion type - "convertible drive". Press X to change tracks for wheels and vice versa. New hull type - flexible. Allows to fold hull in the half for better passability, esp. in mountains.


- HEAT/HEAT/HE
- 360/360/480 HP
- 260/355/85 mm
- 40/20 mm
- 760 m
- 250 hp

После войны фирма Meili разработала прототип грузовика Meili Flextruck, предназначенного для использования в гористой местности. Грузовик имел сочлененный корпус, позволявший преодолевать препятствия и давший машине лучшую проходимость. В надежде, что такую разработку можно применить в военном деле, был представлен аванпроект истребителя танков. Отличительными чертами проекта, среди прочего, были крайне компактные габариты и отличная проходимость (благодаря сочлененному корпусу). Кроме того, была проработана возможность использования надеваемых гусеничных лент, как на танках БТ. Однако ввиду своей дороговизны, проект был отклонён.
New propulsion type - "convertible drive". Press X to change tracks for wheels and vice versa. New hull type - flexible. Allows to fold hull in the half for better passability, esp. in mountains.


- APCR/APCR/HE
- 390/390/480 HP
- 234/280/53 mm
- APCR/HEAT/HE
- 390/390/480 HP
- 280/360/65 mm
- 40/20/20 mm
- 760 m
- 900 m
- 500 hp
- 530 hp


Бронетранспортёр, разработанный MOWAG на основе БТР Puma и представленный в 1981 году. В качестве вооружения использована башня французского танка AMX-13/105. Серийно не производился.


- HEAT/APCR/HE
- 410/410/500 HP
- 360/430/65 mm
- 40/20/20 mm
- 40/20/20 mm
- 1050 m
- 530 hp
Бронетранспортёр, разработанный MOWAG на основе БТР Puma и представленный в 1981 году. Два экземпляра были переданы в Германию, где специально для них были разработаны два варианта башен. В качестве вооружения использована французская 105-мм пушка. Серийно не производился.


- APCR/APCR
- 180/180 HP
- 336/400 mm
- 10
- 0.3 s
- 30 s
- 20/20/20 mm
- 1050 m
- 275 hp
Piranha была разработана конструкторским бюро MOWAG в начале 1970-х гг. как универсальное шасси для различных боевых и специальных машин с колёсной формулой 4 × 4, 6 × 6 и 8 × 8, с пулестойкими колёсами, обеспечивающими возможность безаварийной езды на спущенных/пробитых пулями и другим повреждающим воздействием шинах. Все представители семейства машин Piranha являются плавающими, для чего оснащены двумя гребными винтами в кормовой части корпуса. Один из вариантов предолагал установку мощнейшей автопушки ARES. Построен в единственном экземпляре.


- 35/35/45 HP
- 60/100/20 mm
- 5 shots
- 5/5/0 mm
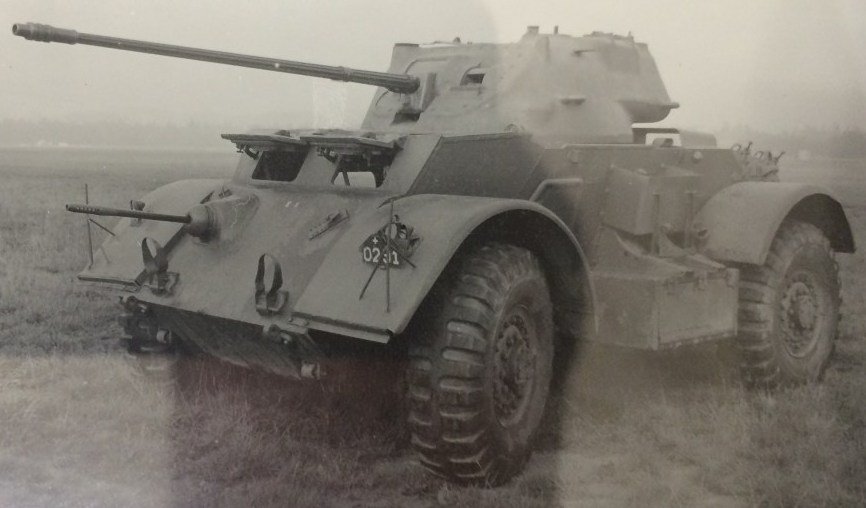

Alternative project version for 34M. Pz.K-41 with the same 34 mm main gun. This SPAAG was not armored. Nothing else is known.

- 12/12/18 HP
- 50/70/10 mm
- 15 shots
- 25/32/32 mm
- 194 hp
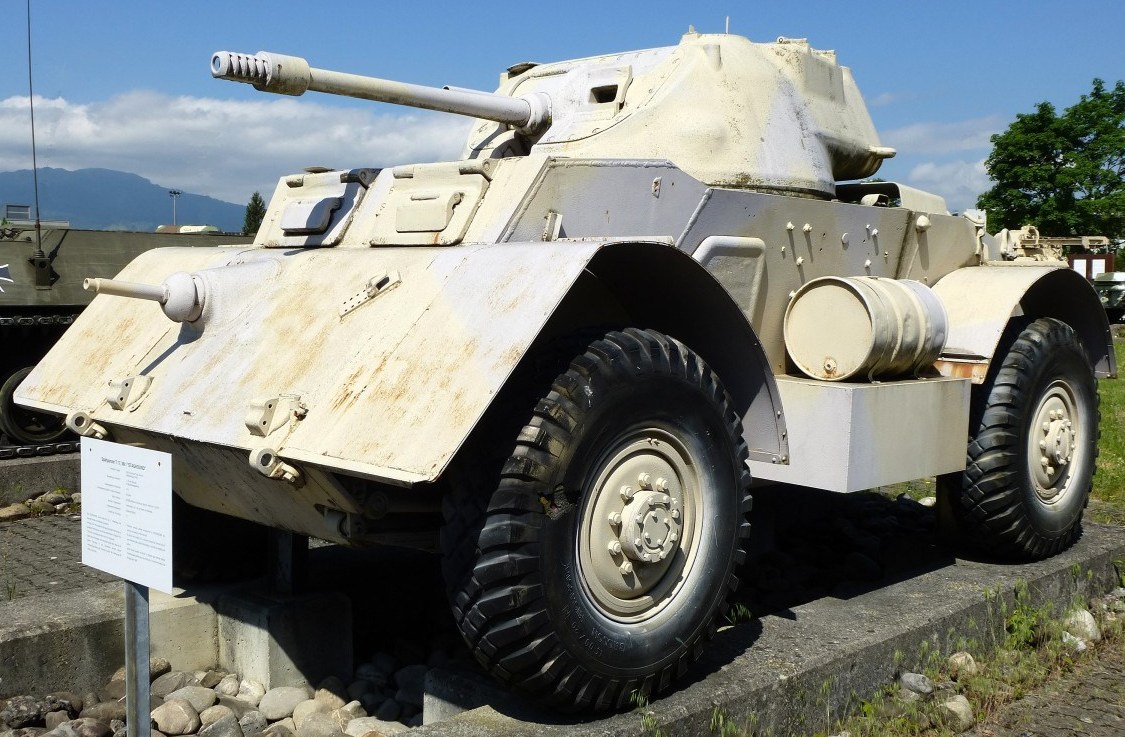
Switzerland purchased 64 Staghounds from Britain in the 1950s. Some of those in Swiss army service were re-armed with 20 mm guns. Five of these Staghounds were turned over to the local K+W ordnance firm to examine more extensive rearmament packages including 47 mm and 90 mm gun upgrades, but these projects did not proceed beyond trials.


- 110/110/175 HP
- 108/154/38 mm
- 110/110/175 HP
- 115/162/38 mm
- 0/0/0 mm
- 94 hp

In the end of 1950s MOWAG produced MR 8 (also known as Wotan) APC in different variants: with autocannons, ATGM or 75 mm / 90 mm guns. MR 8 was built on chassis of MOWAG GW4500 truck (from 1955) and used steering of both axles. Gunned versions didn't go further than prototypes.
MR 8-75 seems to carry the same guns as Nahkampfkanone I. The whole index "8-75" can be not correct, but the vehicle is exactly a part of the MR 8 program.

- 30/30/40 HP
- 99/120/15 mm
- 8-20 mm
- 275 hp
The Mowag family of the armoured vehicle since 1972 is an outstanding export success, reminiscent of the past Swiss pikemen mercenary companies that roamed the battlefields of Europe in the Renaissance wars. This extremely versatile and modular vehicle was produced since 1972 in four derivatives, 4×4, 6×6, 8×8 and even 10×10, all with the same hull, and featured allowing extensive tailorization for any customer, from the engine to the main armament, as well as inexpensive maintenance and reconversions. It has been indeed converted to an air defense vehicle, ambulance, anti-tank vehicle, APC, cargo transport, command & control vehicle, or for electronic warfare, fire support, internal security, mortar carrier, recovery and reconnaissance among other things. It was not uncommon for a customer to purchase the vehicle in a single configuration, then order kits for conversions, and gradually convert obsolescent vehicles for other duties at low cost. The Mowag Piranha (From the famous Amazon river Characidae) was exported to 21 countries and also largely built under license as nowadays it is estimated that more than 10,000 Piranha-based vehicles are in service worldwide.
The most famous of them all, the 8×8 is by far the best known and most common. It is also perhaps the most produced 8×8 APC in the Western world, with more than 6,500 vehicles for this version alone. It was by any standards an influential model that spawned dozens of licensed versions, also inspiring a whole genre over five continents. This includes the concept of wheeled IFVs and destroyers that are popular today in many armies, as they can replace costly MBTs in low-intensity conflicts and asymmetric warfare.
Piranha I 8X8 D was a Swiss experimental model. It had a new turret with a 30 mm automatic gun and also a remote-controlled turret with machine guns in the rear. It was built in 1976 but seemed to be unsuccessful for unknown reasons (possibly - because it was too complicated and cost much).

- 55/55/70 HP
- 100/140/24 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 130/160/45 mm
- 25/32/32 mm
- ?
- 194 hp
Switzerland purchased 64 Staghounds from Britain in the 1950s. Some of those in Swiss army service were re-armed with 20 mm guns. Five of these Staghounds were turned over to the local K+W ordnance firm to examine more extensive rearmament packages including 47 mm and 90 mm gun upgrades, but these projects did not proceed beyond trials.


- 240/240/320 HP
- 140/190/45 mm
- 0/0/0 mm
- 94 hp

In the end of 1950s MOWAG produced MR 8 (also known as Wotan) APC in different variants: with autocannons, ATGM or 75 mm / 90 mm guns. MR 8 was built on chassis of MOWAG GW4500 truck (from 1955) and used steering of both axles. Gunned versions didn't go further than prototypes.
MR 8-90 was built in 1964 and armed with 90 mm recoilless gun Pak 55. It had a hydraulic gun carriage with a shield which raised during fire and descended to reload the gun.


- 220/220/280 HP
- 120/150/45 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 150/200/45 mm
- 6-12 mm
- 161 hp

In the end of 1950s MOWAG produced MR 8 (also known as Wotan) APC in different variants: with autocannons, ATGM or 75 mm / 90 mm guns. MR 8 was built on chassis of MOWAG GW4500 truck (from 1955) and used steering of both axles. Gunned versions didn't go further than prototypes.
MR 8-90 was built in 1964 and armed with 90 mm recoilless gun Pak 55. It had a hydraulic gun carriage with a shield which raised during fire and descended to reload the gun.

- 240/240/320 HP
- 200/260/45 mm
- 20/15/15 mm
- 240 hp
MOWAG Pirat with an improved turret. Only one prototype was built.

- 12/12/18 HP
- 39/50/10 mm
- 15 shots
- 40/40/45 HP
- 52/74/18 mm
- 25/15/15 mm
- 110 hp
- 125 hp
Originally planned for Lithuania as LTL, LTL-H was offered to Swiss by Praga as per their requirements. Further evaluations led to development of LTH, which later entered the Swiss service as Panzer 39.
For Lithuania LTL was to mount either 20 mm Oerlikon autocanon or a 37 mm gun.
Only one prototype of LTL was built in april 1948 as both Lithuania and Switzerland had further specified their requirements, evetualy leading to LTH which entered service as Panzerwagen 39, and LTL for Lithuania (now based off LTH) which were built, but never delivered (USSR happpened to Lithuania before that) and eventualy ended up as LT-40s in fascist Slovakia.

Almost the same as in the French branch, but with a weaker gun
- 30/30/36 HP
- 29/46/18 mm
- 40/40/40 mm
- 82 hp
Switzerland as many other countries before the WW2 interned 12 R-35's that crossed the French border in June 1940.


- 14/14/20 HP
- 101/140/10 mm
- 15 shots
- 110/110/175 HP
- 120/160/38 mm
- 210 hp
- 280 hp
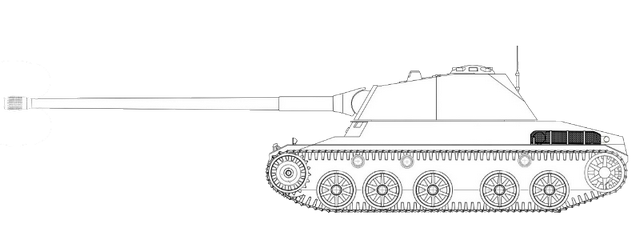
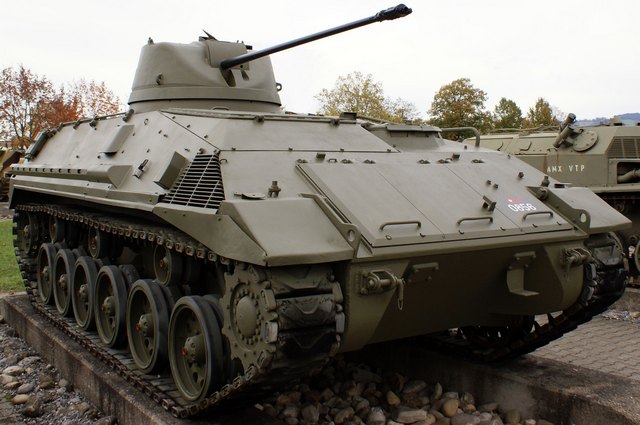
The Saurer Tartaruga (Turtle) was a prototype of an armored personnel carrier from the Adolph Saurer AG. The Saurer Tartaruga was built in 1959. Together with the Mowag Pirat it was tested by the Swiss Army. But unexpectedly the Swiss Army decided to buy the American M113. A prototype is now in the Thun tank museum. Also there was a projected version armed with 75 mm tank gun.

- 240/240/295 HP
- 203/237/44 mm
- 185/80/80 mm
- 690 hp
Switzerland received the Tiger II with the Henschel turret in 1945/46 as well as other german tanks and trialed them. It is currently getting restored to working order.

- 135/135/175 HP
- 144/202/38 mm
- 4 shots
- 40/20/20 mm
- 250 hp
The swiss army obtained AMX 13-75s in 1951 and called them Leichter Panzer 51.
- 320/320/420 HP
- 240/300/60 mm
- 260 hp
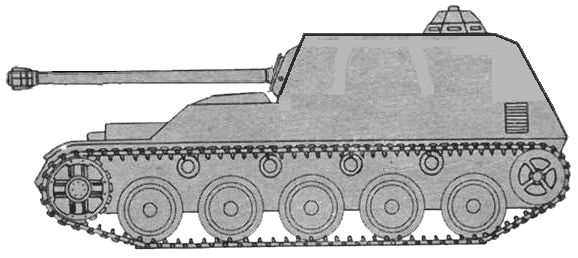
Much less known project of rearming MOWAG Pirat with a 105 mm gun. Unlike the basic Pirat this is a casemate TD. I suppose that it was declined because of overweighting the chassis with too heavy gun.
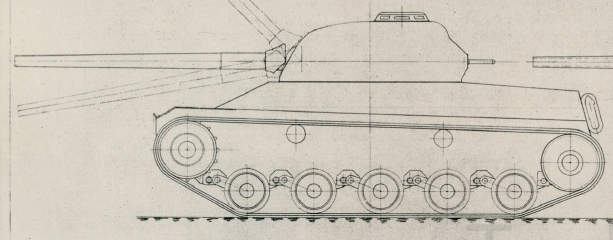
Similar to the Laupen 16t, this version however had a completely indigenous hull planned unlike the 16t, which was based on the G-13.
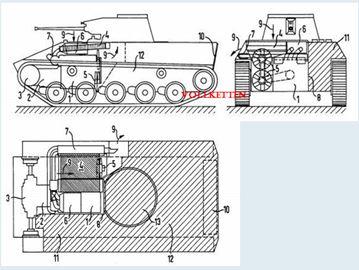
- 240/240/320 HP
- 150/210/45 mm
- 60/25/? mm
- 220 hp


The Laupen tanks are two light tank projects which have been found at the Swiss National Archives, dating from 1950. These designs were meant to be able to defeat the Soviet IS-3 heavy tank which had shocked the western world in 1945, while still being light enough to be able to traverse the hilly landscape of Switzerland. At that time, the best tank the Swiss had was the Panzer 39, a version of the pre-war Panzer 38(t). This tank was clearly obsolete, and the Laupens were meant to replace it. Just as importantly, the AMX 13 was being developed in France. Simply buying this light tank from abroad would have arguably been less expensive than putting a tank industry up from scratch. In the end, the Swiss bought the AMX 13 and the G-13 remained in service as it was. The Laupens faded into history, quietly forgotten on a shelf in the archives.

To simplify, this is the ingame HWK 12 but with 20 mm autocanon.

- 14/14/20 HP
- 60/100/10 mm
- 15 shots
- 20/15/6 mm
- 211 hp


Two prototypes of HWK 13 were built in 1963. They were supposed for export. Mexican army was about to order 40 such AFVs, but refused after the presentation of these two vehicles.


- 240/240/320 HP
- 161/195/45 mm
- 75/45/26 mm
- 100/60/30 mm
- 400 hp
- 400 hp
- 600 hp

Swiss proposal for up armoring the swedish lansen light tank. Variante C featured the biggest improvement in the armor and would have added a lot of weight. Thus another engine and suspension were suggested.

- 40/40/50 HP
- 101/135/20 mm
- 10 shots 2x
- 0/0/0 mm
- 250 hp
An experimental anti-aircraft vehicle based on Panzer 51 (AMX-13) chassis possibly built in Switzerland for the French army. Very little info is known - seems like the tank was unsuccessful.
- 390/390/480 HP
- 268/330/53 mm
- 40/20/20 mm
- 250 hp
It’s an AMX 13 Testbed with the Panzer 61’s main gun (L7 clone). It didn't proceed further than the project stage.

- 110/110/175 HP
- 108/154/38 mm
- 120 hp
Early variant of the NK I without the gun encasement.

- 390/390/480 HP
- 268/330/53 mm
- 120/65/40 mm
- 630 hp
Panzer 61 modernized to Panzer 68 standards.


- 445 HP
- 31 mm
- 120 hp
- 150 hp
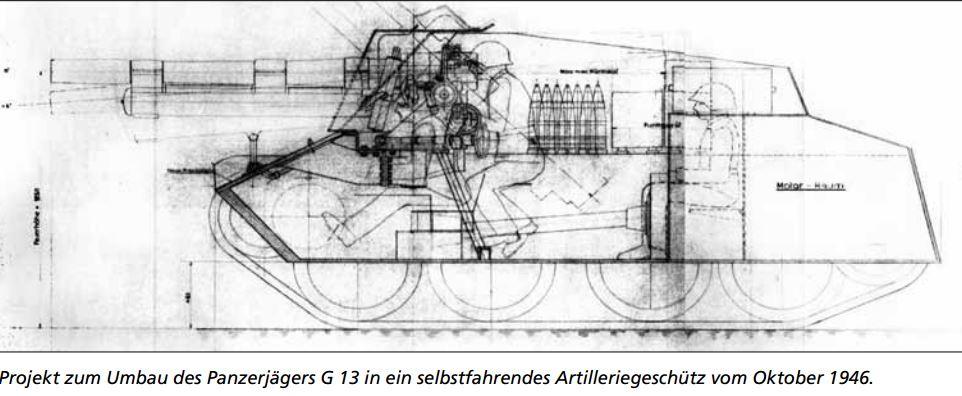
10.5cm Hb.35 L/42 SPG project on the NK I. While Ausf. 1 being the TD version with a closed gun encasement and the Ausf. 2 being the open topped artillery version. Built in 1946, never entered mass production.



- 440 HP
- 28 mm
- 445 HP
- 35 mm
- 540 HP
- 38 mm
- 160 hp

After the war Switzerland planned to build a 10.5 cm SPG project on the chassis of the G-13. Most armor would have been removed in the process.
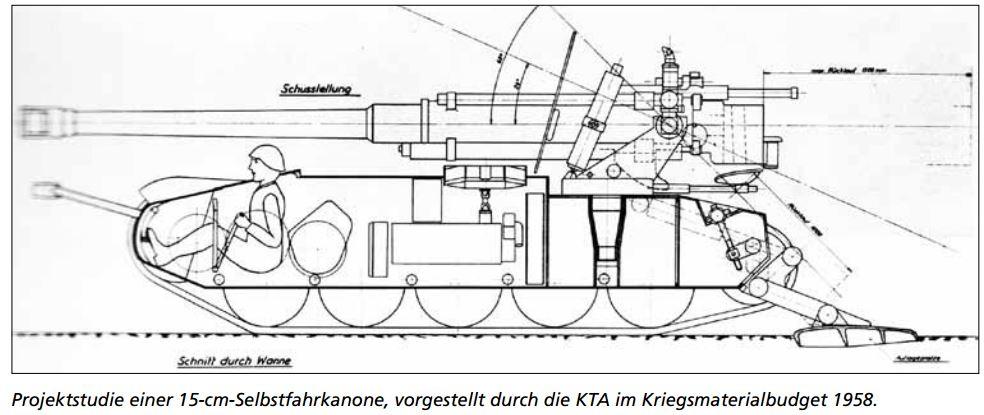

- 690/690 HP
- 42/42 mm
- 250 hp
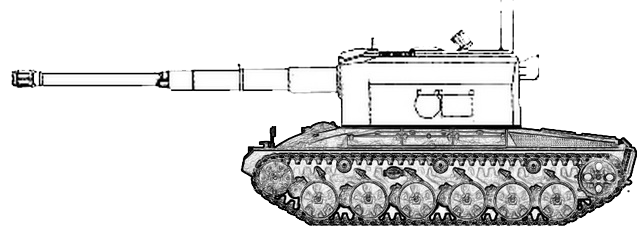
Project for 15cm howitzer on AMX-13 (Panzer 51) hull from 1958. Never built.


- 445 HP
- 35 mm
- 250 hp

Built in france, 4 prototype vehicles were bought for testing in 1959. Tests were discontinued in 1964 and the vehicles never saw mass production.


- 390/390/480 HP
- 290/370/53 mm
According to sources at WG, this after-war project could have different suspension types, both tracked and wheeled. Overally not a lot is known, all we know is that it does mount a 105 mm gun in a half-opened turret.


- 750/750 HP
- 49/49 mm
- 600 hp

Initial project of the Panzerkanone 68. The idea was to take a Panzer 58 chassis and moutn a 15cm Kanone 42/46 in a turret; never built.

Built on either a modified Panzer 61 or Panzer 68 chassis. Only 4 prototypes were built. It was discontinued due to technical difficulties.

- 750/750 HP
- 51/51 mm
- 660 hp
Built in 1968 on either a modified Panzer 61 or Panzer 68 chassis. Only 4 prototypes were built. It was discontinued due to technical difficulties.

- 6/6 HP
- 22/32 mm
- 20/12/12 mm
- 56 hp


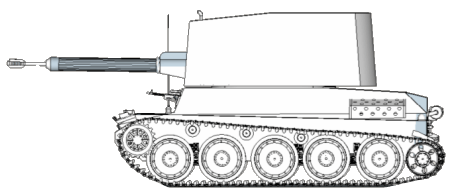

The swiss army bought 6 Vickers-Armstrong Light Tanks Models 1933/34 for testing purposes. Vehicles left service in 1948.

- 6/6 HP
- 22/32 mm
- 50/50/65 HP
- 42/70/23 mm
- 20/12/12 mm
- 56 hp
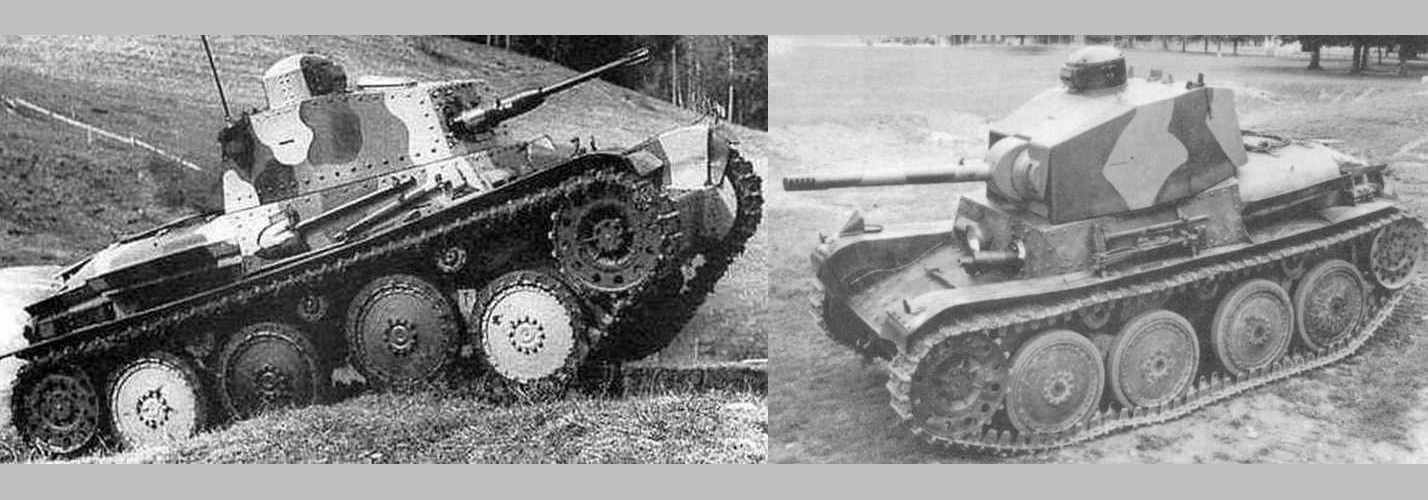

The swiss army bought 6 Vickers-Armstrong Light Tanks Models 1933/34 for testing purposes. Mounting 47mm infantry gun was proposed for the vehicle. Vehicles left service in 1948. If the gun was to be mounted in the real tank, there would have been a couple of minor changes in the turret like seats for the loader and commander (who also doubled as a gunner), a hatch in the rear of the turret and a mount for the gun itself.

Serial Panzer 39 is on the left and the "Neuer Turm" (new turret) is on the right

- 20/20 HP
- 40/65 mm
- 6 shots
- 50/50/65 HP
- 50/78/23 mm
- 60/60/75 HP
- 60/100/24 mm
- 32/15/15 mm
- 50/30/25 mm
- 108 hp
- 125 hp

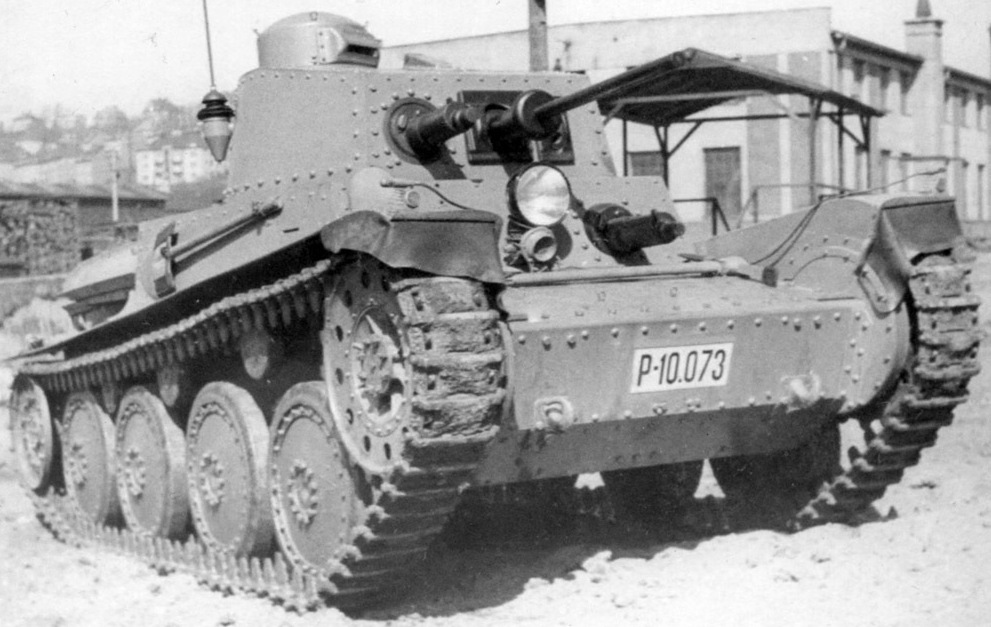
Panzer 39 is a modified version of LTL-H. It's got a new 24mm gun and some other light improvements. The first tanks came to Switzerland in 1939. They served until 1950. In 1946 there was a prototype with upgraded turret and new gun (47 mm), but still it was declined.


- 35/35/45 HP
- 60/100/20 mm
- 5 shots
- 32/20/15 mm
- 125 hp


The Panzer 39L is an elongated Panzer 39 with an additional pair of roadwheels, mounting a 34mm AA gun. Designed in 1941.


- 110/110/175 HP
- 91/138/38 mm
- 410/350 HP
- 45/95 mm
- 75/??/?? mm
- 175 hp
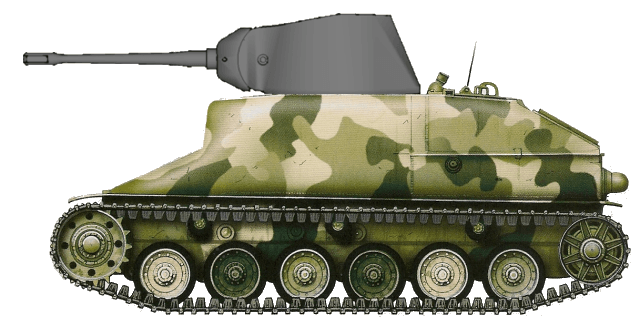

Same as with the Panzer 39L this is an upgraded Panzer 39 chassis and is thought to be a successor to the 39L. It does get more armor than the 39L and additionally it also receives Sideskirts. It gets a completely new turret with decent (up to 75mm of Turret) armor excluding the gun mantle. It was to be equipped with a 7.5 cm Gun L/43 or additionally a 10.5cm Howitzer.


- 14/14/20 HP
- 70/100/10 mm
- 15 shots
- 75/75/95 HP
- 150/200/29 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 180/240/45 mm
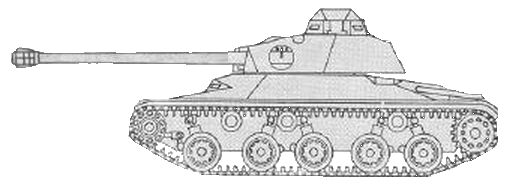
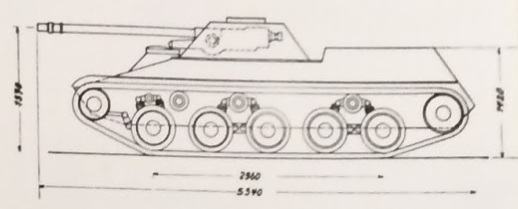
In 1970, Swiss company MOWAG (well known for some interesting designs) designed their own Leichter Panzer with an off-centre engine at the front right hand side and front transmission. Formal name in not known at this time.
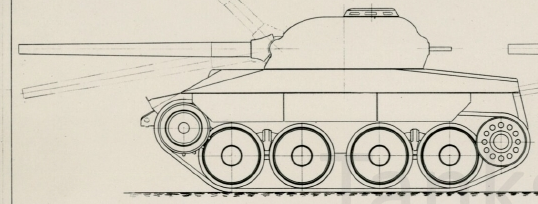
- 240/240/320 HP
- 185/240/45 mm
- 240 hp
A project of Hispano-Suiza in Switzerland to meet the demands for a light tank with good mobility and firepower. Prototyped in 1956. The design of this vehicle was later improved and amended to become the H.S.30.


- 240/240/320 HP
- 170/248/45 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 200/260/45 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 205/267/45 mm
- 30/15/10 mm
- 240 hp
- 240 hp
This tank destroyer was built on the multipurpose HS 30 hull, developed in Switzerland by Hispano-Suiza. Several vehicles utilizing this hull were in West-German service - amongst them being the Schützenpanzer-lang IFV as well as self-propelled mortars, tank destroyers and other light vehicles. It was constructed in 1958, but this particular vehicle was not accepted in service neither in Germany nor in Switzterland. Another project, the Kanonenjagdpanzer HS 30 with the gun installed directly in frontal plate was also not successful - the Bundeswehr adopted the Raketenjagdpanzer I (also built on the HS 30 chassis) instead. The Germans didn't scratch the cannon-armed tank destroyer idea completely, but they built it on another chassis.

First tested in 1957, several prototypes built.

- 240/240/320 HP
- 140/200/45 mm
- 20/15/10 mm
- 20/15/10 mm
- 240 hp
- 240 hp

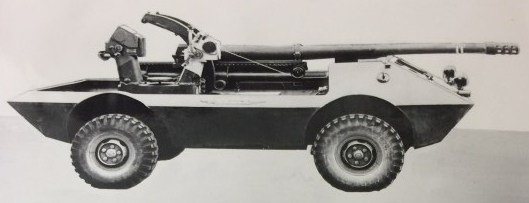
In the 1950′s, the MOWAG company was founded by the inimitable Walter Ruf and started designing a variety of wheeled and tracked vehicles for military and civilian use. Early in the 1950′s, they were testing the MOWAG Pirat, which was a fully enclosed rear turretted tank destroyer, fitted with a powerful 90mm MECAR gun. Later modifications included smoke dischargers and a commander’s cupola added to the turret, two extra return rollers and some automotive changes, which can be seen with the relocation of the exhaust pipe and air vents. This TD is not known to have been adopted.


- 240/240/320 HP
- 207/265/45 mm
- 20/15/15 mm
- 240 hp

This Tank which had one Prototype built, was originally meant as an AA Vehicle. It was also planned to be fitted with other Weaponry like a 90mm Gun if the Trials on the AA Prototype were successful. It handles much like the Pirat and the HS-30, but it’s even lighter (11.3 Tons with a 240 bhp Engine) and at the same time being larger than the Pirat. Only a mockup was built in 1955.

Lightweight version of Laupen 30t.

- 240/240/320 HP
- 207/265/45 mm
- 600 hp

Based on the Laupen 30ton Medium Tank concept from 1950 by the Eidgenössische Konstruktionswerkstätte. This is essentially a Light Tank version of the Medium Tank.


- 110/110/175 HP
- 91/138/38 mm
- 110/110/175 HP
- 120/160/38 mm
- 410/350 HP
- 45/95 mm
- 75/??/?? mm
- 280 hp

Medium/heavy tank based on the chassis on the Nahkampfkanone II.

Tank Project for a 16 ton Tank intended to fight against the Soviet IS-3, Based on the G-13 Tank destroyer.

- 240/240/320 HP
- 150/210/45 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 150/210/45 mm
- 3 shots
- 60/25/?? mm
- 220 hp
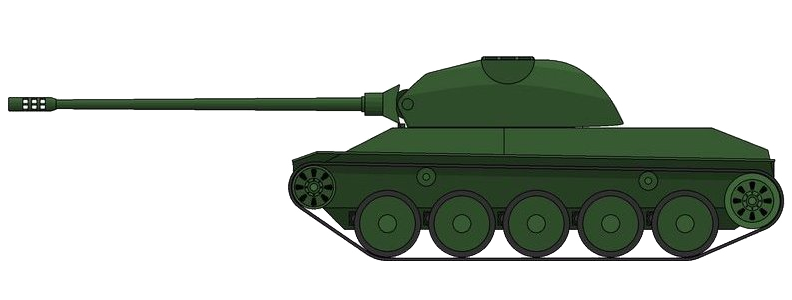

The Laupen tanks are two light tank projects which have been found at the Swiss National Archives, dating from 1950. These designs were meant to be able to defeat the Soviet IS-3 heavy tank which had shocked the western world in 1945, while still being light enough to be able to traverse the hilly landscape of Switzerland. At that time, the best tank the Swiss had was the Panzer 39, a version of the pre-war Panzer 38(t). This tank was clearly obsolete, and the Laupens were meant to replace it. Just as importantly, the AMX 13 was being developed in France. Simply buying this light tank from abroad would have arguably been less expensive than putting a tank industry up from scratch. In the end, the Swiss bought the AMX 13 and the G-13 remained in service as it was. The Laupens faded into history, quietly forgotten on a shelf in the archives.


- 240/240/320 HP
- 160/240/45 mm
- 70/45/45 mm
- 600 hp
- 800 hp


Switzerlands first attempt at building a 30 ton medium tank in 1952, 1 mockup and one prototype were built.


- 230/230/280 HP
- 226/258/42 mm
- 320/320/420 HP
- 210/268/53 mm
- 80/30/20 mm
- 600 hp

After World War II, Switzerland was only equipped with outdated fighting vehicles of foreign production such as the Hetzer. Switzerland sought to purchase new armored fighting vehicles but was unable to do so due to other nations' involvement in the Korean War. Thus, in 1953 funding was allocated for the development of a domestic medium tank. The first prototype was completed by Eidgenoessische Konstruktionswerkstaette in 1957 and was designated as Panzer 58. The main armament of the first prototype was a domestic 90 mm cannon. A second prototype was equipped with a British Ordnance QF 20 pounder. Another ten tanks armed with the 105 mm cannon were manufactured from 1960-1961.


- 240/240/320 HP
- 219/264/45 mm
- 230/230/280 HP
- 226/258/42 mm
- 70/45/45 mm
- 120/65/40 mm
- 600 hp
- 600 hp
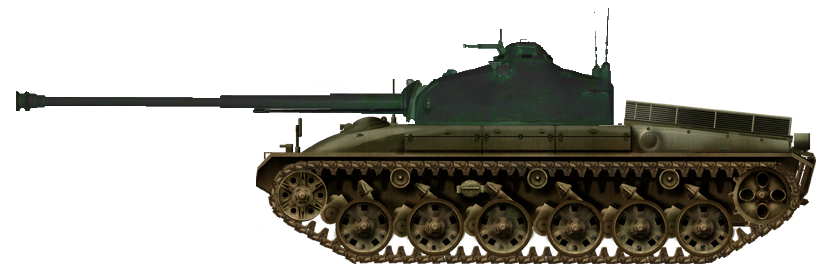
Further development of KW 30/52, with rounded armor due to the influence of the American M48 Patton. It was later renamed to Panzer 58.


- 320/320/420 HP
- 210/268/53 mm
- 390/390/480 HP
- 268/330/53 mm
- 120/65/40 mm
- 630 hp
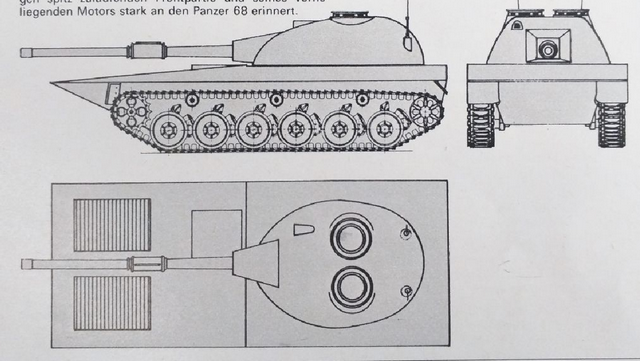
It is the first ever mass produced Tank in Switzerland. Further improvements on Panzer 58 was made which lead to the Panzer 61 such as a better engine, a new Turret design and some other changes to the exterior and interior. It served till the early 1990s.


- 390/390/480 HP
- 268/330/53 mm
- 120/65/40 mm
- 660 hp
Modernisation of the Panzer 61, aside from a more powerful engine and rubber pads on the tracks, not a lot has changed.


- 230/230/280 HP
- 226/258/42 mm
- 320/320/420 HP
- 210/268/53 mm
- 390/390/480 HP
- 268/330/53 mm
- 120/65/40 mm
- 750 hp

Based on an experimental chassis on the Panzer 58 with a 750hp Maybach engine and the Renk transmission, one of the drivetrain options for Panzer 74.

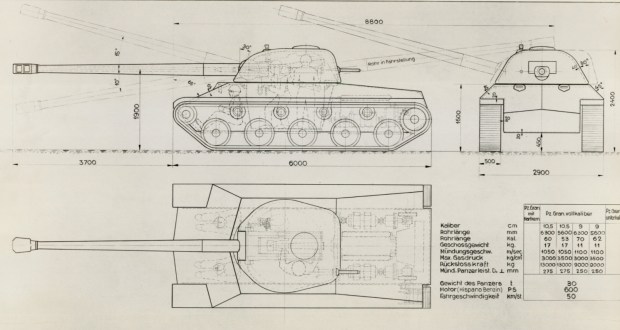
- 390/390/480 HP
- 268/330/53 mm
- 120/65/40 mm
- 660 hp

Panzer 68 Lamborghini is a planned modification on the Panzer 68 which included a new turret and overall better protection. It got the name “Lamborghini” due to its sleek shape.

- 230/230/280 HP
- 226/258/42 mm
- 390/480/480 HP
- 268/210/105 mm
- 152/89/89 mm
- 650 hp
- 720 hp

Switzerland has tried to upgrade their Centurion medium tanks multiple times, such as mounting a more powerful Maybach diesel engine.

- 230/230/280 HP
- 226/258/42 mm
- 390/480/480 HP
- 268/210/105 mm
- 152/89/89 mm
- 650 hp
- 720 hp
- 1100 hp
Another Upgrade made by switzerland to their centurions: this time it would have the drivetrain of the Panzer 74 (VFZ 69) which consisted of the Renk transmission as well as a 1100 hp Maybach MTU MB 837 engine.

- 230/230/280 HP
- 226/258/42 mm
- 75/45/26 mm
- 600 hp
Swiss proposal for up armoring the swedish lansen light tank.

Due to the armor of the KW 30 being to poor, it was suggested to increase its weight by 10-15 tons and increase its armor.

- 240/240/320 HP
- 160/240/45 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 200/275/45 mm
- 170/100/100 mm
- 600 hp
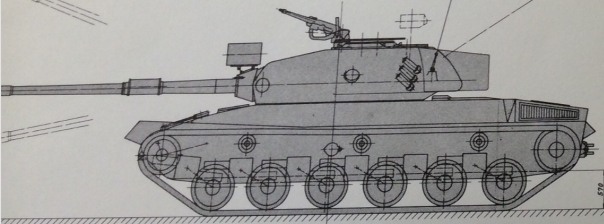
40-45 ton version of KW 30. Due to the KW 30 having very poor armor with the proposed weight of 30 tons, it was suggested that KW 30 would have been uparmored to get a similar amor thickness as the M48 patton, so around 170mm Turret armor and around 110mm- 120mm hull armor frontally and around 75mm side armor. The reason why this never happened is because of the swiss designers figuring out rounded armor around 2-3 years later thanks to the american Patton tanks.

- 320/320/420 HP
- 228/296/53 mm
- 350/40/40
- 600 hp
The first design of what would become the KW 30. While being rather light, it’s frontal protection would have been outstanding.

Designed in 1969, the project itself was called Panzer 74. This vehicle features a smaller turret than the other variants.

- 390/390/480 HP
- 268/330/53 mm
- 420/420/510 HP
- 267/334/61 mm
- 250/100/40 mm
- 250/100/50 mm
- 750 hp
- Hydraulic

The Swiss Panzer 74 was a Main Battle Tank Project started in 1969. It was meant as an upgrade to the Panzer 68 tank then in service with the Swiss army, as it had begun to be regarded as underarmored for its time. New, better protected and better armed main battle tanks were entering service, tanks like the Soviet T-64, the British Chieftain and the American M60 Patton. Between the 1950’s and 1980’s, the Swiss military philosophy called for Main Battle Tanks with good mobility, without sacrificing too much in terms of firepower and protection. The Panzer 68 was the latest vehicle in the Swiss tank lineage, being derived from the previous Panzer 61 and the little-produced Panzer 58. However, recently introduced designs made the Panzer 68’s armor seem obsolete. While the Panzer 74 presents itself as a capable vehicle which would have improved Switzerland’s armored capabilities, it never went past the design phase. The main reason for this was likely that it would have been too expensive and the Swiss politicians realized that building a completely new tank wasn’t worth it, as Switzerland was not in any grave danger. The Panzer 68 was viewed as sufficient and it stayed in service with various upgrades until 2003.

Featuring a larger turret and an automated loading system.

- 390/390/480 HP
- 268/330/53 mm
- 420/420/510 HP
- 267/334/61 mm
- 250/100/50 mm
- 750 hp
- 1200 hp
- Hydraulic
The Swiss Panzer 74 was a Main Battle Tank Project started in 1969. It was meant as an upgrade to the Panzer 68 tank then in service with the Swiss army, as it had begun to be regarded as underarmored for its time. New, better protected and better armed main battle tanks were entering service, tanks like the Soviet T-64, the British Chieftain and the American M60 Patton. Between the 1950’s and 1980’s, the Swiss military philosophy called for Main Battle Tanks with good mobility, without sacrificing too much in terms of firepower and protection. The Panzer 68 was the latest vehicle in the Swiss tank lineage, being derived from the previous Panzer 61 and the little-produced Panzer 58. However, recently introduced designs made the Panzer 68’s armor seem obsolete. While the Panzer 74 presents itself as a capable vehicle which would have improved Switzerland’s armored capabilities, it never went past the design phase. The main reason for this was likely that it would have been too expensive and the Swiss politicians realized that building a completely new tank wasn’t worth it, as Switzerland was not in any grave danger. The Panzer 68 was viewed as sufficient and it stayed in service with various upgrades until 2003.


- 35/35/45 HP
- 60/100/20 mm
- 5 shots
- 10/10/10 mm
- 120 hp

Early version of NK I, being an AA SPG. It uses prolonged Panzer 39 chassis as well. Archive documents say that it's even been built. Different canons were proposed: 34mm (the priority gun for the project) , 47mm and a 75mm howitzer.

- 50/50/65 HP
- 60/78/23 mm
- 110/110/175 HP
- 42/85/38 mm
- 10/10/10 mm
- 120 hp
Early version of NK I, being an AA SPG. It uses prolonged Panzer 39 chassis as well. Archive documents say that it's even been built. Different canons were proposed: 34mm (the priority gun for the project) , 47mm and a 75mm howitzer.


- 110/110/175 HP
- 108/154/38 mm
- 110/110/175 HP
- 115/162/38 mm
- 120 hp
- 150 hp


The designed heralded from early experiments made between 1943 and 1944 in Switzerland in the design and construction of an armoured vehicle. The Nahkampf cannon 1 was built onto the chassis of the armoured car Panzerwagen 39, Panzer 38(t) type LTL-H CSSR armoured fighting vehicle. The chassis was extended by a roller produced by the company Berna in Olten. Since only a few parts were available, it was partially constructed using parts of armoured cars, mainly the chassis and transmissions. The armour consisted of only thin sheet metal and, in initial experiments, only a 75-millimeter cannon was installed. The prototype was used by the Swiss Army with the car plate (M + number 7236).

G-13 tank destroyer bought from Czechoslovakia recieved some upguning proposals.

- 110/110/175 HP
- 110/158/38 mm
- 135/135/175 HP
- 144/202/38 mm
- 160 hp

G-13 is a post war version of the Jagdpanzer 38 built for Switzerland, armed with a StuK 40 gun. There also was a G-13 version that would have the same gun as the AMX 13 75. Whether it had an autoloader or if it was loaded by hand is not known.

Tank destroyer built in 1946. It was mounted with various real and mockup guns during it’s lifetime. It can be found at the Panzermuseum Thun in Bern.

- 110/110/175 HP
- 115/162/38 mm
- 135/135/175 HP
- 152/198/38 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 160/240/45 mm
- 910/700 HP
- 86/150 mm
- 300 hp

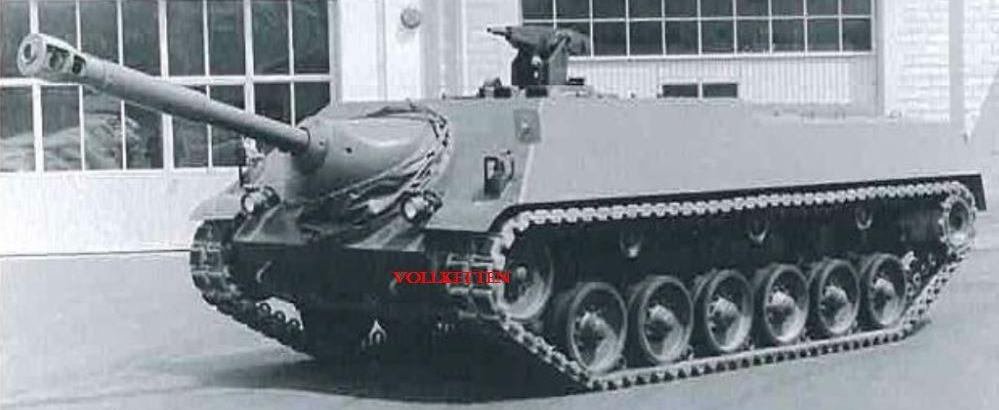
The hull and the superstructure were made of cast steel by the Georg Fischer AG. The construction of the chassis was by Saurer in Arbon, the assembly of the chassis at Berna in Olten and the design and installation of the gun of the K + W in Thun. Driver, commander and the horizontal gunner sat side left, right vertical gunner and loader. The gun was mounted in a hull based superstructure and had only a limited traverse arc, so the entire vehicle had to turned onto the target before the gun itself could be aimed. The gun barrel could be retracted for travel. Four different types were planned, but one prototype was made and that did not see service; only driving tests were made in Thun from 1946 to 1947 for testing in troop deployment. Development was stopped in 1947.


- 135/135/175 HP
- 152/198/38 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 160/240/45 mm
- 910/700 HP
- 86/150 mm
- 320/320/420 HP
- 228/296/53 mm
- 300 hp

Same as Nahkampfkanone II, however II B would have a layer of 15mm spaced armor all over it’s frontal armor which was actually a real proposal back in 1946 in order to make the shape of the vehicle more even.


- 240/240/320 HP
- 238/250/102 mm
- 390/390/480 HP
- 268/330/53 mm
- 500 hp
- 550 hp
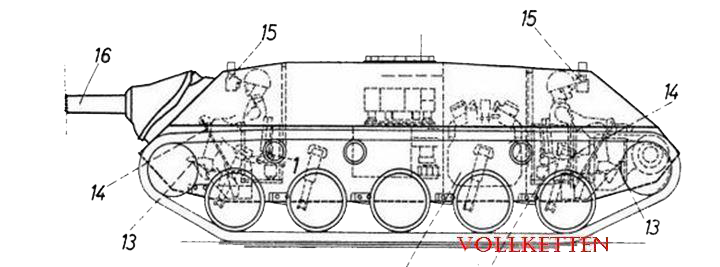
This vehicle basically uses the hull and layout of the German Jagdpanzer Kanone and is listed under several names – it was called the HM-13, Gepard and Cheetah. MOWAG called it the Gepard, although the prototype was known for a while as the HM-13. Some sources state that the first Jagdpanzer Kanone were built in Switzerland and then sent to Germany, others that the Gepard was licence-built, it is not clear whether the Swiss version used this extra driver position. The first of such vehicles in Switzerland were built in the period between 1960 and 1962.


- 240/240/320 HP
- 238/250/102 mm
- 390/390/480 HP
- 268/330/53 mm
- 550 hp

Kanonenjagdpanzer version designed by MOWAG engineer Walter Ruf. It’s more or less the same as HM-13, aside from the fact that it does have two drivers, one in the front and one in the rear. It had the intention to drive backwards just as fast as it could forwards.


- 390/390/480 HP
- 268/330/53 mm
- 420/420/510 HP
- 267/334/61 mm
- 575 hp
By the mid to late 1970′s, work continued at MOWAG on a new tank destroyer using the Taifun Mk.I chassis, which was used for a wide variety of spin-off vehicles of all classes, of which the best known is this vehicle called the Taifun. It featured a modular gun system and had very good mobility. Only one built. It has been scrapped.

- 90/90/110 HP
- 140/200/29 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 180/250/45 mm
- 10/10/10 mm
- 10/10/10 mm
- 240 hp
- 260 hp
By 1957, MOWAG company was offering a small light tank destroyer under the name “Skorpion”, fitted with a 57mm AT gun and later modified to carry a 90mm gun. Neither of these projects was liked very much or accepted in service, although the gun and the mount found their use later on a variety of wheeled vehicles. By 1960 or so, the name has changed to ‘Pirat’ and various changes were made to the vehicle, even thought it remained open-topped and still carried the powerful 90mm MECAR gun.

Laupen 30t armed with 9 cm guns.

- 240/240/320 HP
- 176/238/45 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 200/275/45 mm
- 200/40/? mm
- 600 hp


The design of the Panzer 58 started back in 1950 when the Swiss government quickly noticed that the AMX 13s that they had ordered were insufficient and that they needed a medium tank as well. The political situation all over the globe meant that getting a foreign medium tank would have been difficult, which meant that designing their own tank was necessary. As a result, they designed a 30ton Tank which was the great grandfather of the Panzer 58. This 30t Panzer design though never left this stage of development and was subjected to refinement until it became the KW30/52 which is the first official KW30 design.

Laupen 30t armed with 10.5 cm guns.

- 240/240/320 HP
- 200/278/45 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 250/315/45 mm
- 390/390/480 HP
- 245/306/53 mm
- 390/390/480 HP
- 260/326/53 mm
- 200/40/? mm
- 600 hp
The design of the Panzer 58 started back in 1950 when the Swiss government quickly noticed that the AMX 13s that they had ordered were insufficient and that they needed a medium tank as well. The political situation all over the globe meant that getting a foreign medium tank would have been difficult, which meant that designing their own tank was necessary. As a result, they designed a 30ton Tank which was the great grandfather of the Panzer 58. This 30t Panzer design though never left this stage of development and was subjected to refinement until it became the KW30/52 which is the first official KW30 design.

Early stage of the NKPz tank development

- 240/240/320 HP
- 210/260/45 mm
- 390/390/480 HP
- 245/290/53 mm
- 400/400/515 HP
- 230/290/61 mm
- 40/30/30 mm
- 630 hp
- 660 hp

The NKPz or Neuer Kampfpanzer was developed by Contraves in the mid 1970s to meet a Swiss Army requirement for a new main battle tank. The new MBT was intended to replace an ageing fleet of 320 Centurions, used by the Swiss Army. The NKPz was a very advanced MBT design at that time. However in the early 1980s Swiss government decided to build German Leopard 2 main battle tanks under license. These tanks were 15%-30% cheaper comparing with the NKPz, but also inferior. Layout of the NKPz was similar to Israeli Merkava. This main battle tank had a wedge-shaped hull and a front-mounted engine for better protection. The rear part of the hull was intended for ammunition storage.

Early stage of the NKPz tank development - with 105 mm L7 gun.


- 390/390/480 HP
- 245/290/53 mm
- 390/390/480 HP
- 268/330/53 mm
- 70/40/30 mm
- 1100 hp
The NKPz or Neuer Kampfpanzer was developed by Contraves in the mid 1970s to meet a Swiss Army requirement for a new main battle tank. The new MBT was intended to replace an ageing fleet of 320 Centurions, used by the Swiss Army. The NKPz was a very advanced MBT design at that time. However in the early 1980s Swiss government decided to build German Leopard 2 main battle tanks under license. These tanks were 15%-30% cheaper comparing with the NKPz, but also inferior. Layout of the NKPz was similar to Israeli Merkava. This main battle tank had a wedge-shaped hull and a front-mounted engine for better protection. The rear part of the hull was intended for ammunition storage.


- 240/240/320 HP
- 239/284/45 mm
- 240/240/320 HP
- 235/280/45 mm
- 3 shots
- 50/30/30 mm
- 600 hp
- 630 hp

Actually nothing is known about the Chansard tank series, but they mostly seem to be NKPz early stages of development.


- 240/240/320 HP
- 220/270/45 mm
- 390/390/480 HP
- 245/290/53 mm
- 30/30/30 mm
- 600 hp
- 630 hp

Actually nothing is known about the Chansard tank series, but they mostly seem to be NKPz early stages of development.


- 240/240/320 HP
- 210/260/45 mm
- 390/390/480 HP
- 245/290/53 mm
- 60/40/40 mm
- 630 hp
- 750 hp

Actually nothing is known about the Chansard tank series, but they mostly seem to be NKPz early stages of development.


- 400/400/515 HP
- 260/328/61 mm
- 100/60/40 mm
- 750 hp

Actually nothing is known about the Chansard tank series, but they mostly seem to be NKPz early stages of development.


- 30/30/40 HP
- 90/110/15 mm
- 20/15/15 mm
- 240 hp

Flakpanzer A.14 was a light anti-aircraft vehicle built in 1955 based on HS 30 AFV - when the Swiss Army needed modern AA forces. A.14 was designed in two versions: with double 30 mm guns (this one) and double 20 mm in a bit changed turret. It was overally fine, but had problems aiming jet planes - actually, even aiming in their direction because it didn't have a radar search system, which was a serious problem. Thus the vehicle was abandonned - waiting for the next more successful swiss AA machine.