Israeli tech tree for World of Tanks proposal by Pablo Escobar
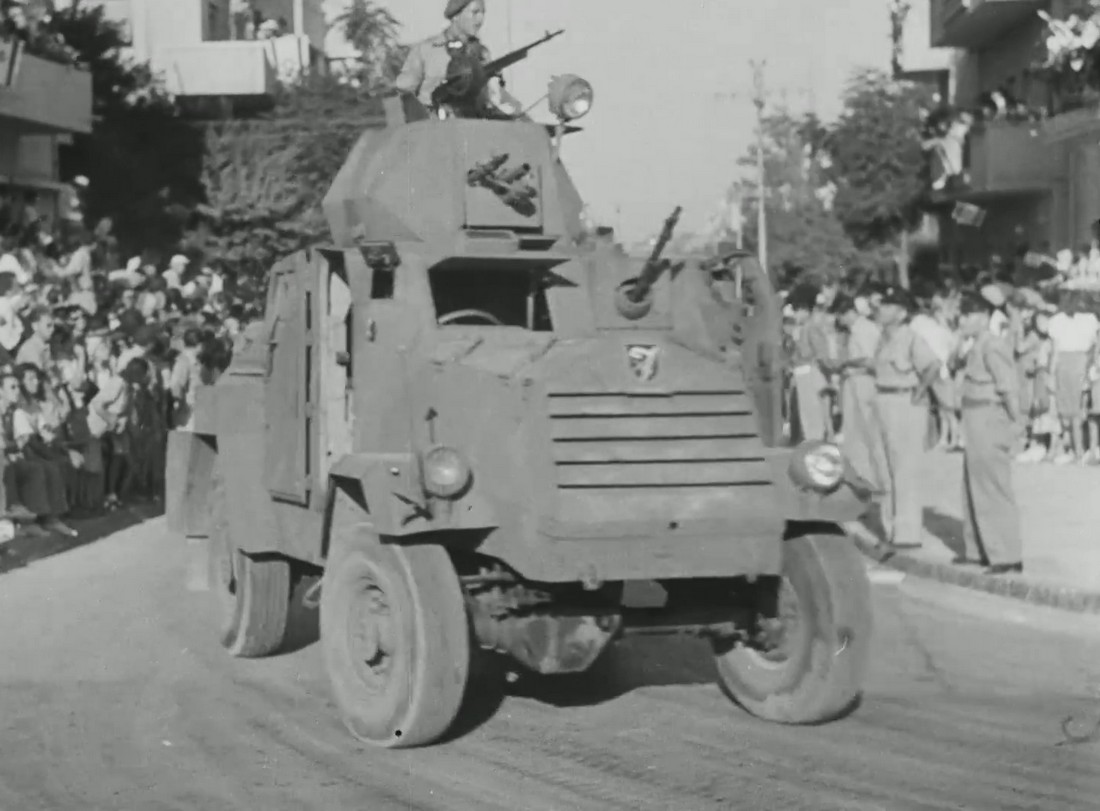

- 6/6/6 mm
- 104 hp



- 6/6/6 mm
- 110 hp
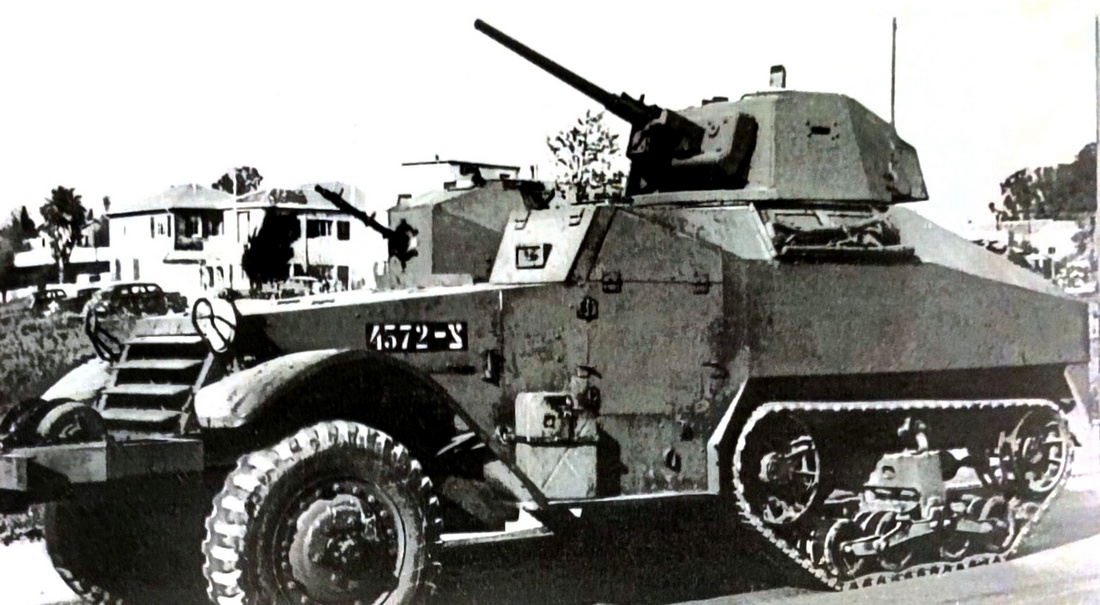




- 6/6/6 mm
- 12/12/12 mm
- 148 hp
- 148 hp



- 76/51/51 mm
- 89/51/51 mm
- 450 hp
- 500 hp

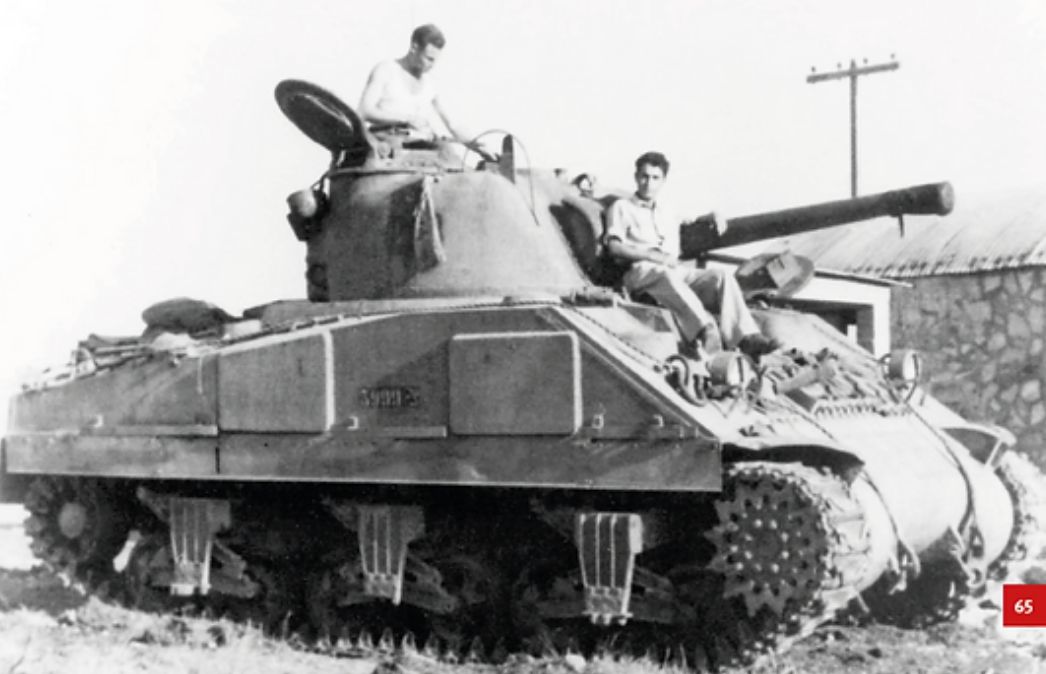
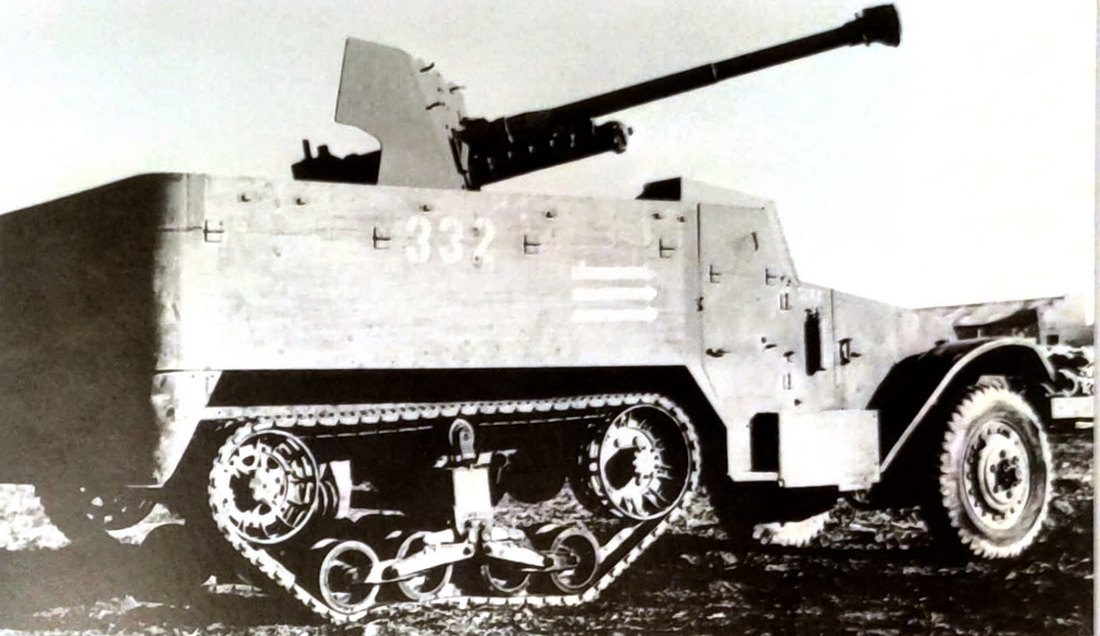
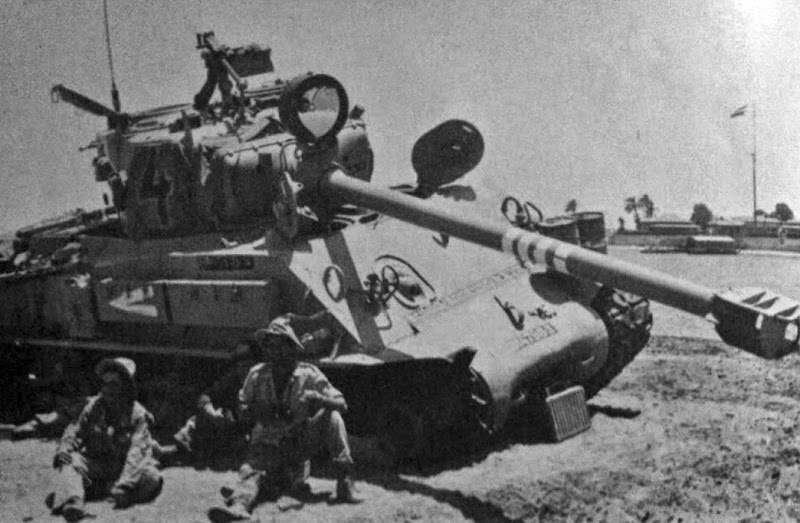
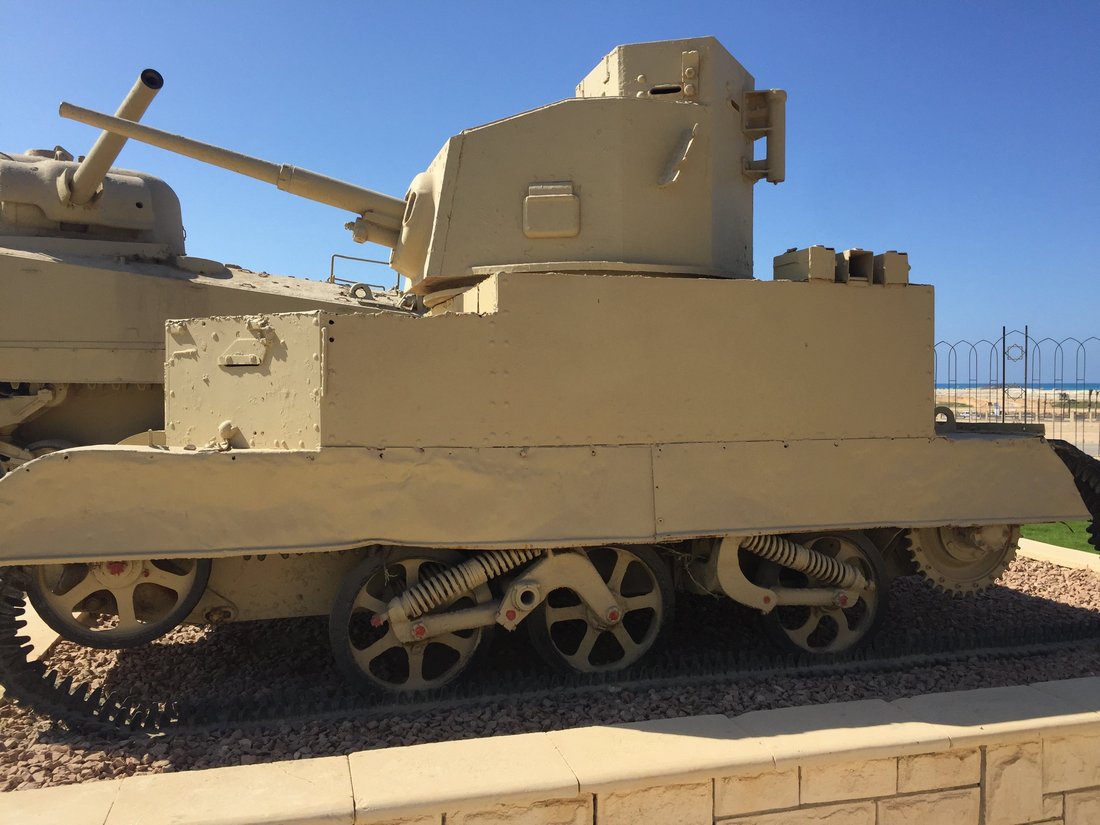
This vehicle combines three real prototypes: Meir (armed with 20 mm HS 404), Sherman with 76 mm M1916 howitzer and Sherman with 75 mm Krupp's howitzer.
1). M4A2 Sherman "Meir"
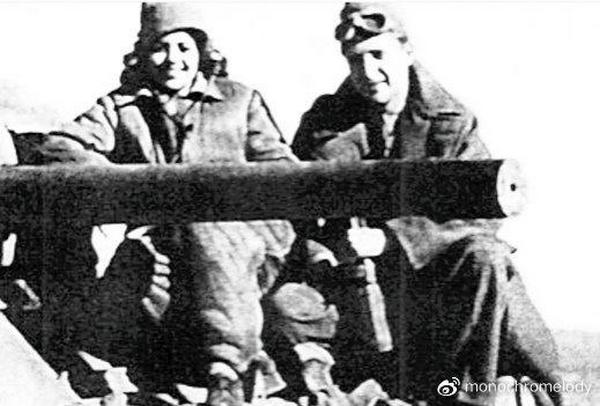

During World War II, the tank served in British forces, but by 1947, it was stored in Haifa, awaiting either transport to the UK or destruction as the British withdrew from Palestine. The intended method of disposal was crude—simply pushing it off a cliff to render it irreparable. However, this particular M4A2 (designated Sherman III in the UK) escaped that fate.
The Haganah militia, later to become the IDF, bribed British personnel £2,000 to acquire the tank instead. However, it was little more than an empty shell—its gun had been removed, sighting equipment was missing, the engine was inoperative, and even the tracks were absent. Undeterred, the Haganah transported the tank to Tel Aviv, where the British had left behind an armoured vehicle repair facility. While most essential equipment was found there, some parts had to be scavenged from various sources. Considerable effort was required to get the engine running, and the missing tracks—likely the original ones—were discovered buried in the sand.
Despite these efforts, a crucial component was still missing: the main gun. Initially, the tank was used for training without armament, effectively functioning as an oversized, heavily armoured personnel carrier. However, the need for a functional weapon was clear. The solution came in the form of a 20mm Hispano autocannon, salvaged from a gunnery training site. Ingeniously, it was mounted inside the original 75mm gun tube, making the modification nearly invisible. The tank was then renamed "Meir" after the girlfriend of one of its crew members.
"Meir" saw action during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, fighting alongside Cromwell tanks that had also been acquired through bribery and the assistance of a defecting British soldier. Still lacking a proper main gun at the time, it was ultimately damaged in the Battle of El Arish in 1948. To prevent its capture, it was sabotaged and abandoned—the first and perhaps most unique Sherman the IDF ever possessed, lost to history.
2). Sherman with 76 mm M1916 howitzer:


IN DEV

- 76/51/51 mm
- 89/64/64 mm
- 350 hp
- 400 hp

The M-1 Sherman (sometimes called "Super Sherman", though the name is generally associated with M-50 variants) was the mainstay of the IDF forces in the 50's. Most of the Israeli M1 Shermans seem to be the M4A1 variants, but there are also pictures of the M4A3E8 and even some M4A4 variants with custom-mounted E8 suspensions. Generally, the M1 variant was in service until the late 50's, when the Shermans were converted into the M50 Super Sherman standard.


- 76/51/51 mm
- 350 hp
- 400 hp
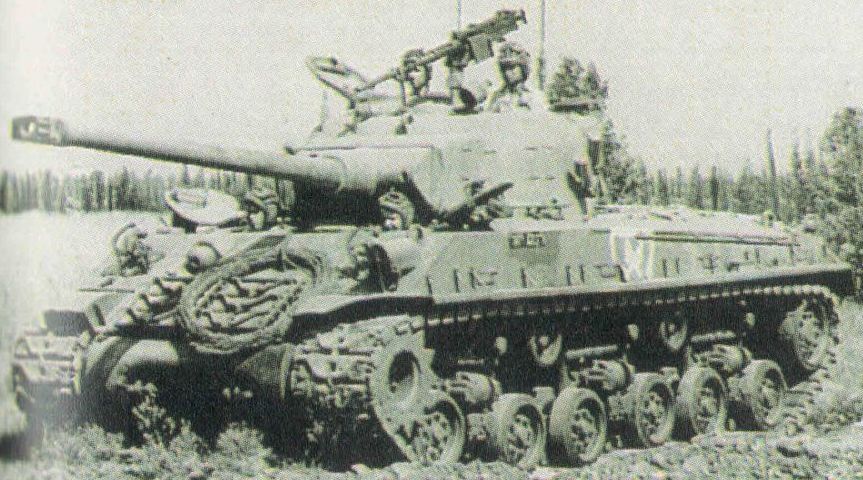

The origin of the program started in 1953 when an Israeli delegation visited France to examine the promising AMX-13 light tank. Although they were not convinced by the thin armor of the vehicle, the gun attracted their interest. Eventually, the Israeli government decided to purchase no less than 400 of these and to devise a mobility-based tactical use alongside the Shermans in service. These tanks would serve extensively during the Sinai campaign. The AMX-13 gun being the high-velocity 75 mm gun CN 75-50 (a development of the German 7.5 cm KwK 42 L/70 of the Panther tank), it was decided to rearm a large portion of the Shermans in the inventory with this piece of ordnance. An order was placed in France in 1955 and an experimental marriage of a M4A1(76) turret with the new gun was shipped in Israel to be tested. The next year, in March 1956, the Israeli Ordnance Corps began conversions in new facilities with the large supplies of the French gun purchased in the meantime.
The result of this conversion was named officially Sherman M-50, although it was also known outside Israel as the “Super Sherman”. This marriage looked like the ww2 British Firefly in essence and had similar performances. The old 1944 M4(75) turret was kept but a large counterweight was added to the rear of the basket. A first batch of 50 conversions on M4A4(76)s was delivered all with VVSS suspensions and Continental R-975 gasoline engines. But these were not especially successful. The weight of the gun added some stress on the engine, resulting in breakdowns, as well as compromised the stability and reduced mobility. So the next conversions were all performed on Diesel versions (Cummins V-8 460 horsepower) and HVSS suspensions. For this reasons, these conversion batches were known as the M-50 Continental or Mk.I and M-50 Cummins or Mk.II. In total 300 Sherman tanks were so converted into M50 until 1964.
M-50 tanks were used in the Suez Crisis (1956), the Six Days War (1967) and the Yom Kippur War (1973).


- 76/51/51 mm
- 76/51/51 mm
- 460 hp


Finnish turret and 75 mm gun for Israeli Shermans:


- 76/51/51 mm
- 76/51/51 mm
- 460 hp
- 535 hp

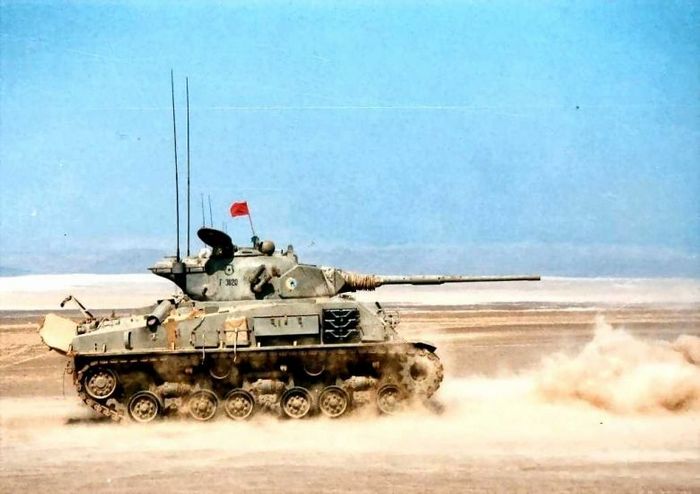
In the 1960s, 180 Sherman tanks received the even more powerful French 105 mm Modèle F1 gun. The barrel length of the gun was reduced from 56 caliber to 44 and it was equipped with a unique double-baffle muzzle brake; ammunition was altered to use a smaller cartridge. In Israel the gun was designated M-51 and the tank the Sherman M-51. M4A1 hulls and the larger T23 turrets (from 76 mm armed Shermans) were used for the conversion. All tanks were fitted with Cummins diesel engines and HVSS suspension. The tank was displayed to the public for the first time during the Independence Day ceremony in 1965.
Both the M-50 and M-51 saw combat in the Six-Day War that left the Golan Heights, the West Bank, and the Sinai peninsula in Israeli hands, often fighting against Soviet World War II-era armor like the T-34-85 (for example at the Battle of Abu-Ageila). Both were also employed in the 1973 Yom Kippur War alongside and against much more modern tanks. The use of such seemingly obsolete tanks was necessary given the desperate nature of the fighting. In combat against the Arab armies, the M-51 proved itself capable of fighting newer, heavier tanks like the Soviet-built T-54/55/T-62. The M-51's 105 mm gun could penetrate these adversaries using HEAT ammunition. The M-51 served well during its time, and is regarded as an excellent example of how an obsolete tank (the Sherman) can be upgraded beyond the limits of its original capabilities.
About 100 of the remaining tanks of this model were sold to Chile in the late 1980s. Some of those were fitted with the IMI-OTO 60 mm Hyper Velocity Medium Support (HVMS) gun. This variant was never used by the IDF. Chile used its Shermans until 1999, when they were replaced by the Leopard 1.




- 130/76/51 mm
- 130/76/51 mm
- 750 hp
- 963 hp



- 178/76/51 mm
- 750 hp
The next, actually, pre-prototype stage of Merkava (built somewhere before 1970 as well), but this time with functional turret and armament from M48 Patton (or Magach if it's Israeli). Seems to be the last stage before the actual Merkava Prototype with its own turret. It's still more like a testbed than something called prototype.

- 38/25/25 mm
- 85 hp



- 45/40/40 mm
- 45/40/40 mm
- 120 hp



- 152/89/89 mm
- 152/89/89 mm
- 750 hp
- 963 hp




- 148 hp
- 148 hp



- 148 hp
- 148 hp



- 148 hp
- 148 hp



- 148 hp
- 148 hp



- 148 hp
- 148 hp



- 148 hp
- 148 hp
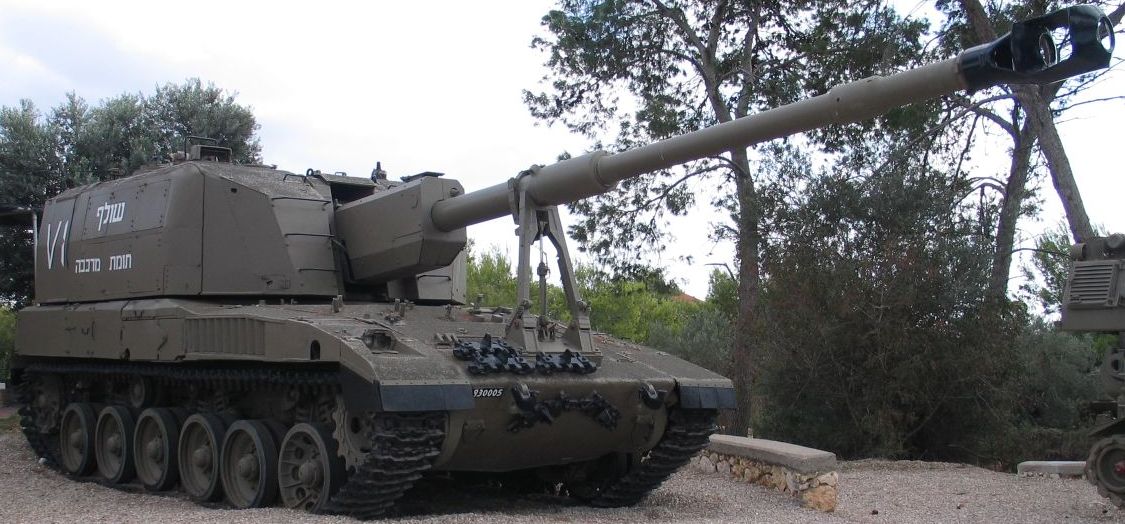


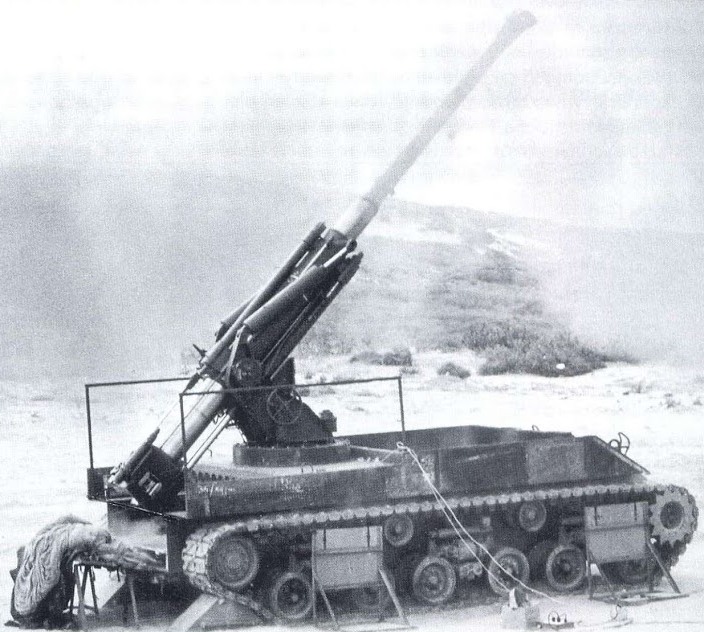
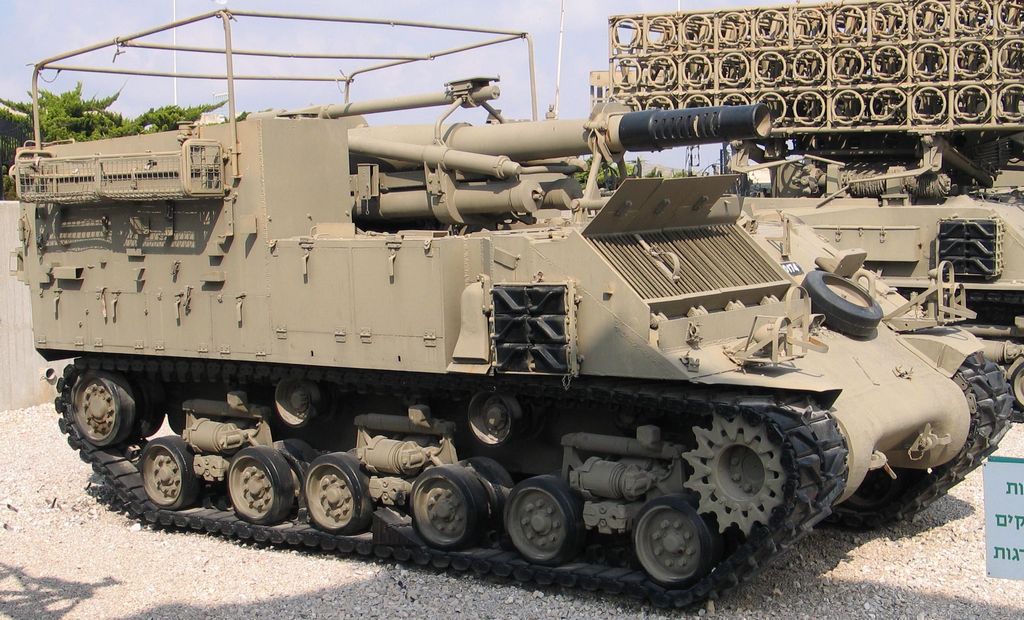
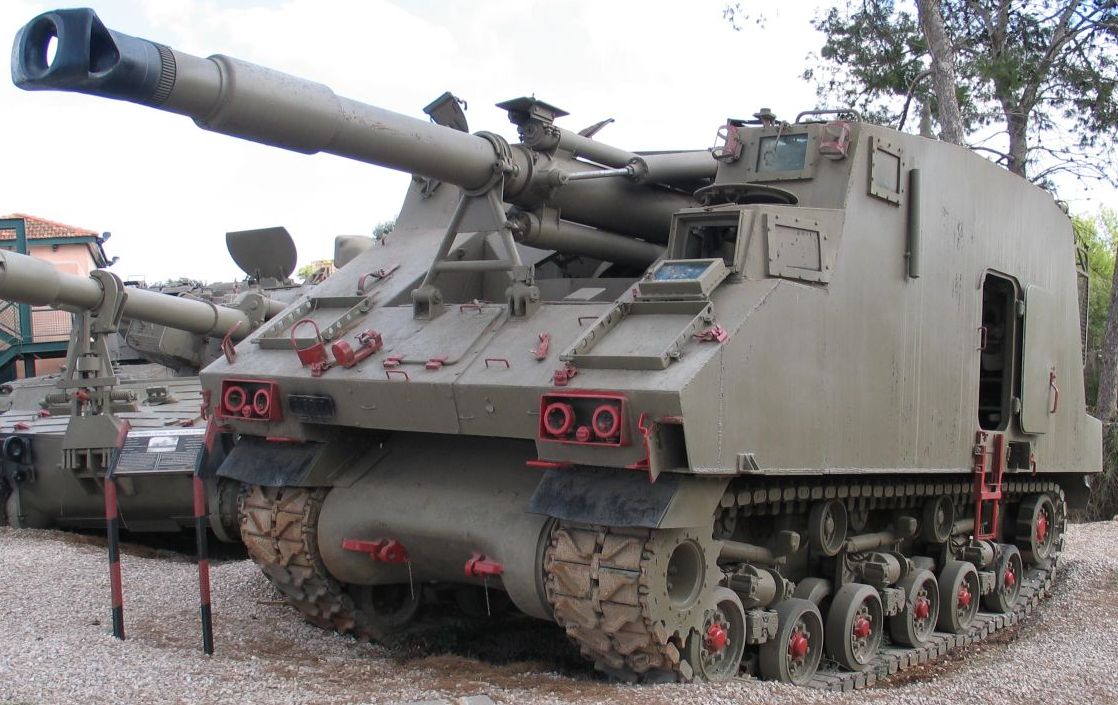
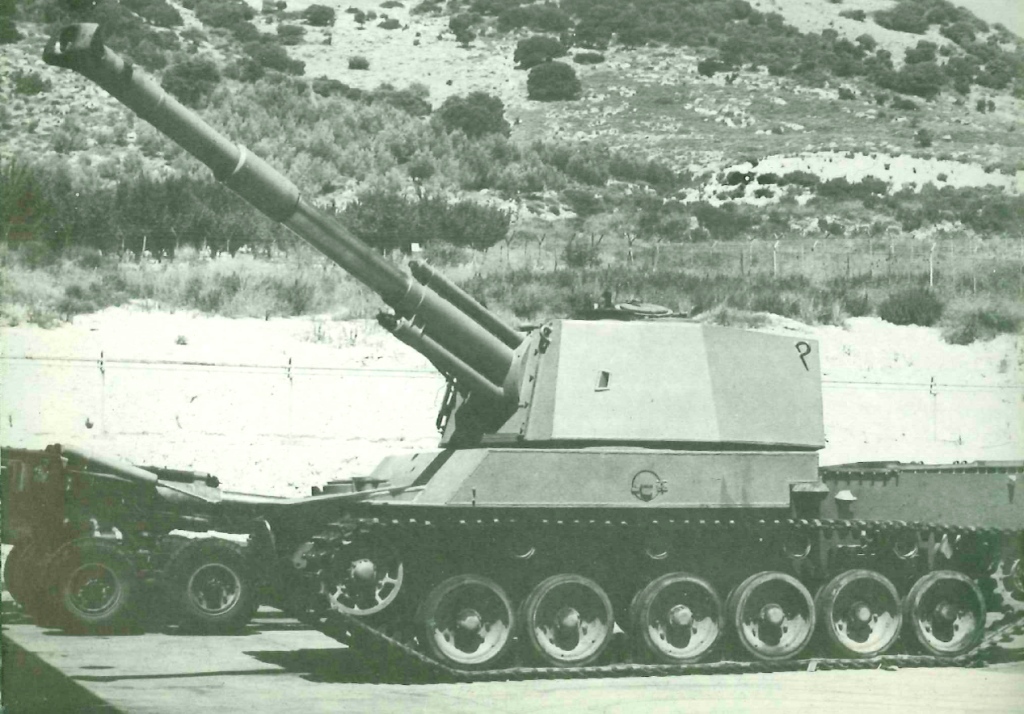
An Israeli prototype self-propelled howitzer developed by Soltam Systems during the 1980s. Based on a modified Merkava Mk.1 chassis, the Sholef incorporated numerous advanced systems into the vehicle, notably GPS, inertial navigation, and a fire control computer. Despite the project being prioritised by the IDF, it was ultimately cancelled in the early 1990s due to high cost.

- 2
- 35/35/35 mm
- 900 hp
The Sholef is an advanced SPH based on the hull of the Merkava Mk.1 MBT. Although the chassis lacks any composite armour, it is still quite thick and sloped enough that it can take some hits from kinetic rounds. However, just like any other modern SPH, the Sholef's turret is large and thin, making it a juicy target for anyone. In terms of firepower, the Sholef has access to an autoloader and powerful conventional HE shells.

The PT-71 is a 1990s modernization for the old Soviet amphibious tank PT-76, upgrading every single aspect of the vehicle except armor. The PT-76-2000 receives a new Detroit Diesel 6V-92T 300hp engine, X-200 transmission (optional upgrade), new Knight FCS, a new Cockerill Mk.3 90 mm gun with a wide selection of ammunition (including APFSDS), and more small upgrades.
- 15/15/15 mm
- 300 hp