Hungarian tech tree for World of Tanks proposal by PikPikker
- 36/36/42 HP
- 40/70/18 mm
- ?
- 100 hp
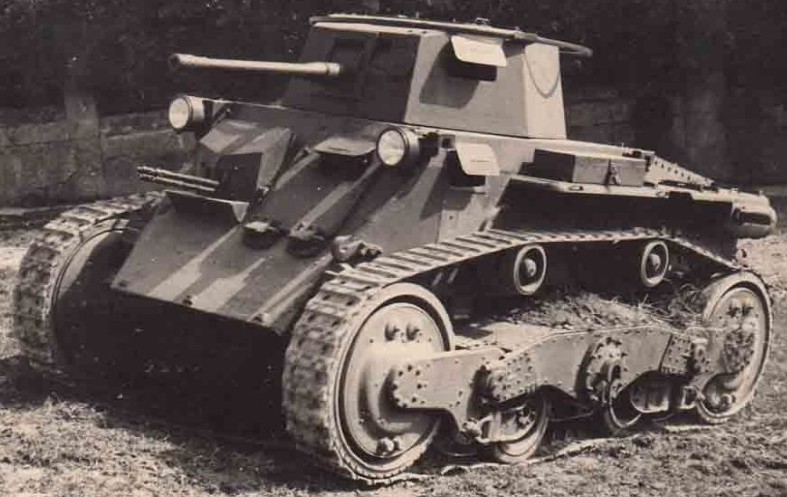

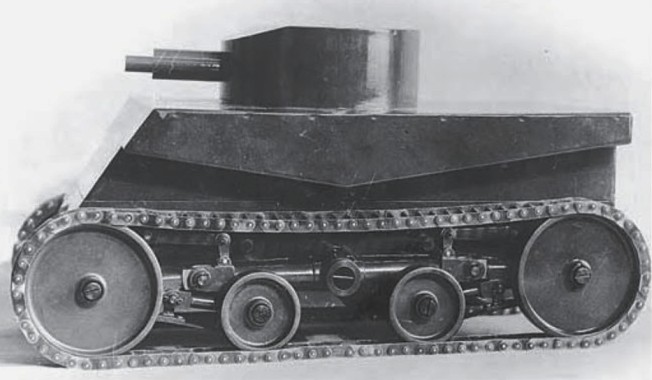
The first project of the V-3 tank was created in 1933. It was designated as an "agricultural tractor" due to Hungary wasn't allowed to keep any armored forces. The army liked the proposal and allowed for one V-3 prototype to be built. The prototype was finished in summer 1935. V-3 itself didn't have a turret, but it likely was projected (similar to the early V-4 turret) and there was a circular hole in the roof of the tank. Mostly V-3 was successful, so it proceeded to the next stage of a fully-equipped tank V-4. In fact, V-3 could drive without tracks and there was its amphibious version.

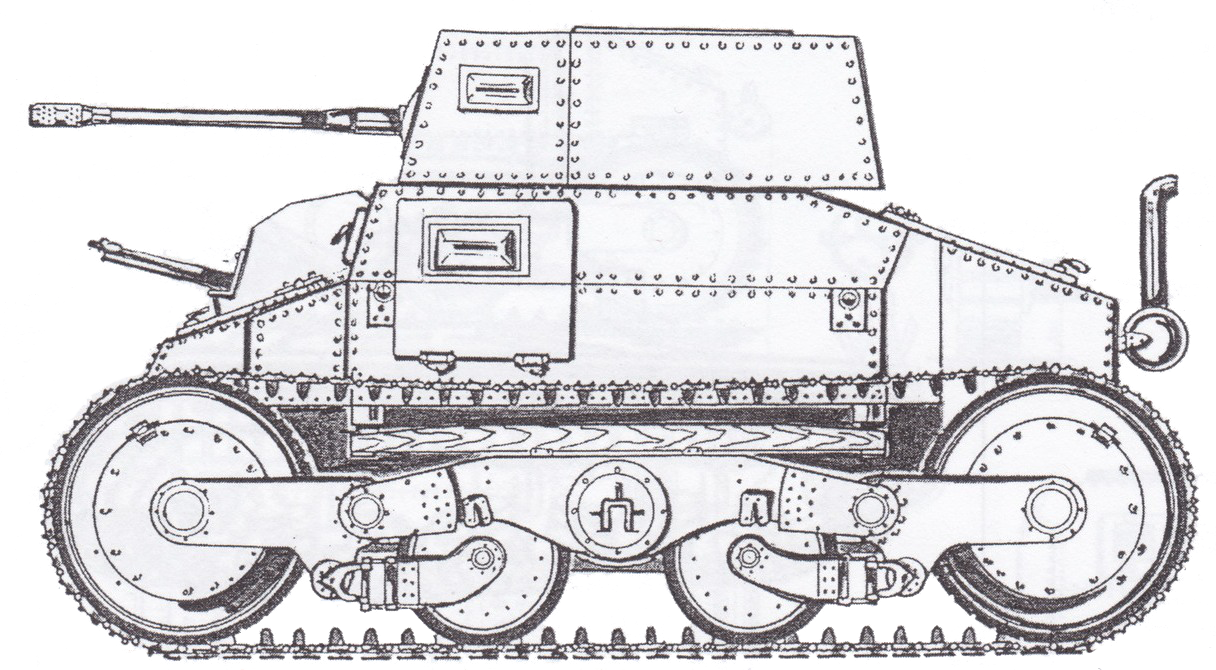
Notice that there are important differences between V-4 and V-4/40: their hulls aren't 100% equal and also they have different crew.

- 36/36/42 HP
- 40/70/18 mm
- ?
- 100 hp
- 160 hp
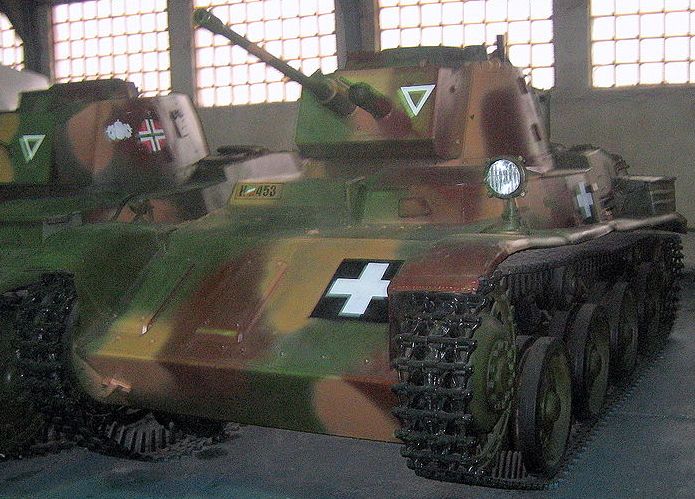


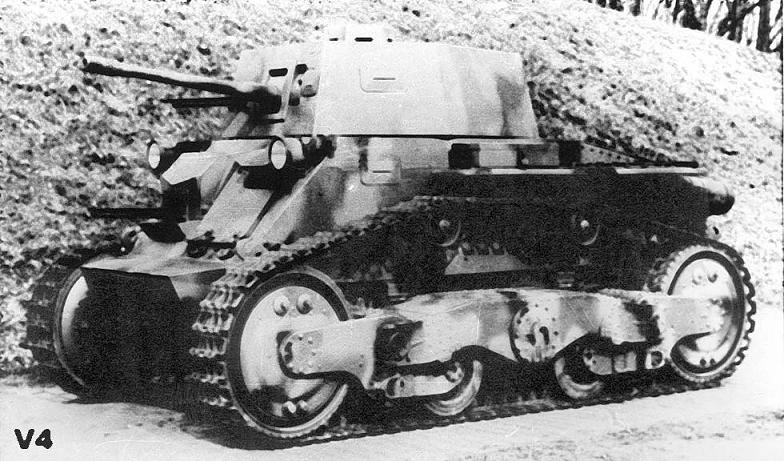
V-4 was the next prototype (seems to be the only built vehicle) made by Straussler. It was built in 1936 and by that time it got a turret with a gun. Actually it was a "short" stage between V-3 and V-4/40 as it became clear that 40 mm gun needed instead.

- 36/36/42 HP
- 39/70/18 mm
- ?
- 160 hp
In 1935 a special version of V-3 tank was offered for export to Japan, but the Japanese was not interested. Exact specifications are unknown, but it should be something like other V-3/V-4 tanks.
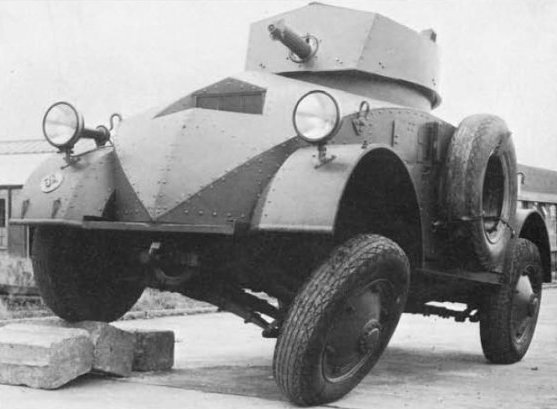


- 12/12 mm
- 65/100 mm
- 10 rounds
- 9/9/9 mm
- 90 hp

The 39M Csaba emerged from an agreement signed with the Weiss Manfred factory of Csepel, Budapest, after Straussler’s design had been rejected by the British army. It was closely based on the Alvis C2. This was an independent suspension four-wheeled vehicle with a conventional framework wrapped in 9 mm (0.35 in) riveted armor plates in a sloped, lozenge shape, as can be seen from a front view. The protection was sufficient against small arms fire and shrapnel, but the main task of this vehicle was reconnaissance, not engaging enemy units. However, its armament was quite potent compared to the protection, with a 20 mm (0.79 in) Solothurn autocannon, also used by the first Toldi tank, comparable to the gun used by the German Panzer II. This was completed by a coaxial 8 mm (0.31 in) Gebauer 37/38M machine-gun, while a second one could be attached to a special AA mounting in the rear hatch of the turret. Normal provision was 200 rounds for the main gun, and 3000 for the machine-guns. The German Ford, 8cyl, 90 hp, 3560 cc engine was coupled with a 5 forward, 5 reverse gearbox, and carried 135 l of gasoline. It could climb a 30 degree slope and 1 meter (3.28 ft) high vertical obstacle, and had a 0.5 m (1.64 ft) maximum fording depth.
After successful trials, the Hungarian army decided to place an order for sixty-one vehicles, named after the year of introduction (39M). By 1940, a further order of forty followed. Half were later converted as the 40M command version, equipped with a R-4T long-range radio at the expense of the 20 mm (0.79 in) gun. This model was recognizable due to its large lattice mast. Production, according to some sources, was scheduled to restart in 1944 at Weiss Manfred, but apparently never did, although some recovered vehicles could have been repaired and refitted there in the meantime.
The first 61 39M vehicles equipped the 1st and 2nd Mechanized Brigades, the 1st and 2nd Armored Divisions and the First Mountain Brigade. A squadron consisted of 10 vehicles, one command 40M and two training vehicles. The section of a mountain brigade consisted of three 39Ms. Except for the mountain brigades, the aforementioned units participated in Operation Barbarossa.
In December 1941, these units were reorganized and brought back from the front, with only 17 surviving Csabas. Combat experience showed that the weaponry and armor protection were insufficient for anything but reconnaissance. In December 1942, on the Don, the first Cavalry Brigade lost almost all its vehicle, 18 Csabas in all. In April 1944, the second Armored Division counted 14 armored cars and was transferred to the Eastern front in August, but over 12 Csabas returned home. By the summer of 1944 the Army was left with 48 combat-ready armored vehicles. Four Csabas formed a section, of which one was a command one. These sections were assigned to four Hungarian infantry divisions. In June 1944, these sections fought in Galicia with the cavalry divisions, with 8 out of 14 returning from the fight. From the autumn 1944 their numbers gradually decreased. None seem to have survived the war.
- 45/45/60 HP
- 39/60/18 mm
- 10-20 mm
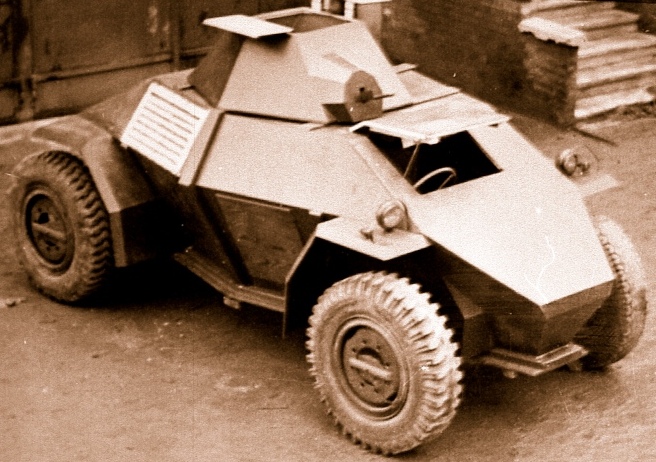
This is how looks the first proposal of the Straussler light tank from 1934 which is the predecessor of V-3/V-4 tanks. Actually its stats and type of planned gun are unknown.
Notice that there are important differences between V-4 and V-4/40: their hulls aren't 100% equal and also they have different crew.
- 36/36/42 HP
- 40/70/18 mm
- 45/45/60 HP
- 64/80/20 mm
- ?
- 160 hp
- 180 hp
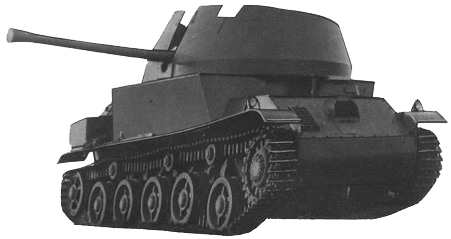
V-4/40 is the ultimate stage of V-3/V-4 tanks. The main change was a new 40 mm Bofors gun. In 1938 previous V-4 was renamed to V-4/40 and rebuilt with new gun and engine. But during the shooting tests V-4 couldn't aim in moving because of very stiff suspension, which was a disappointment to both the army and Straussler. By that time Hungarian army was allowed to order 110 tanks, but V-4 couldn't be a competitor for Pz. I and Landsverk L-60 (which won the contest, becoming the Toldi later). V-4, which stayed in Hungary being useless anymore, was captured by the Red Army in 1945.
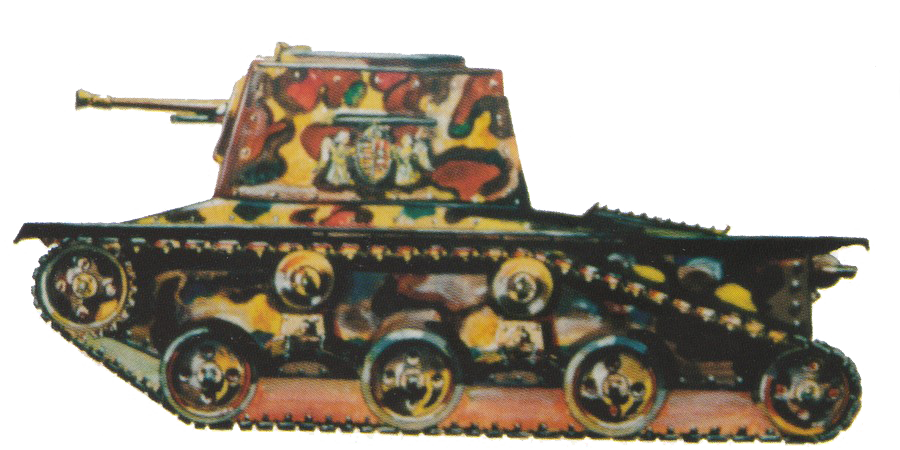

- 45/45/60 HP
- 64/80/20 mm
Light tank proposal from the late 1930s by the Hungarian inventor Jeno Fejes. These characteristics are approximate, because both them and the fate of the project are unknown.

- 45/45/60 HP
- 64/80/20 mm
- 35/13/13 mm
- 155 hp
In 1943, in order to increase the armor of the Toldi IIA against anti-tank rifles, the Hungarian Institute of Military Science made some experiments with installing German “Schürzen”-like additional side armor plates on its hull and turret. However, the experiments showed that these additional armor plates did not provide a lot more protection compared to the gained weight and reduced mobility. After the failed trials, the project was cancelled.
- 50/50/60 HP
- 63/101/23 mm
- 4 rounds
- 13/10/10 mm
- 155 hp
Swedish self-propelled anti-aircraft gun that was developed specifically for Finland between 1941 and 1942. The vehicle was developed from the L-60 m/38 tank. The chassis was lengthened and an 40 mm Bofors AA-gun added. The gun was called 40 ItK/38 in Finnish service. The tank was exported to Hungary, where it was further developed into an AA-tank called 40M Nimrod.
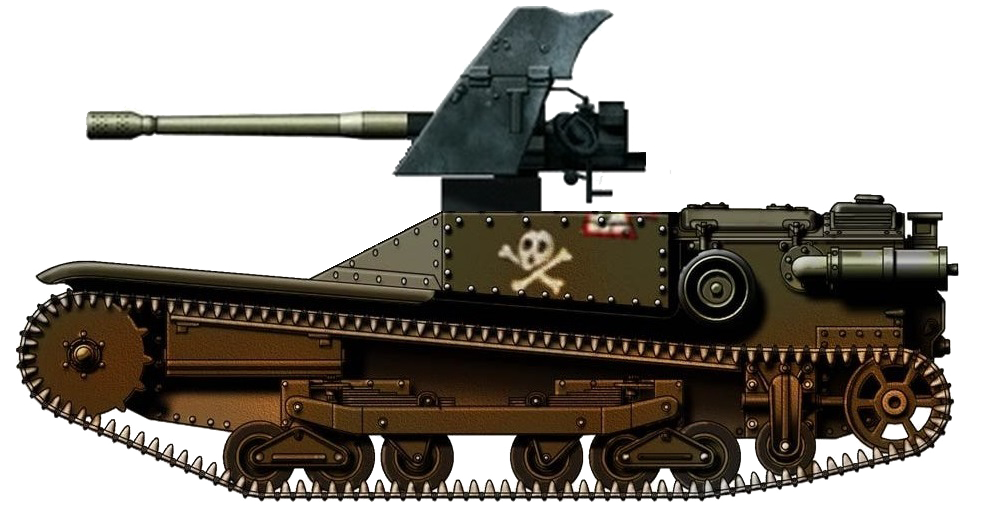

- 45/45/60 HP
- 64/80/20 mm
- 40 hp
- 43 hp
The mass produced 35M. Ansaldo tankette, the slightly modified, is Hungarian version of the Italian CV. 35 or L3/35.
In 1940, another suggestion appeared to arm the obsolete Ansaldos with an anti-tank or field cannon, like the Italians did with their L3s. The suggested gun was the 37 M. 40mm tank gun, which was originally designed for the Straussler V-4, 110 barrels were already even manufactured for it. Later, these guns were used in the conversion of the Toldi IIs to Toldi IIAs. However, the Hungarian Institute of Military Science (HTI) noted that such up-arming would be only possible, if the obsolete and worn-out suspensions of the 35M. Ansaldos would be repaired and/or modernized. Such process would have been definitely not too economical, so the plan was abandoned even before the experimental stage.
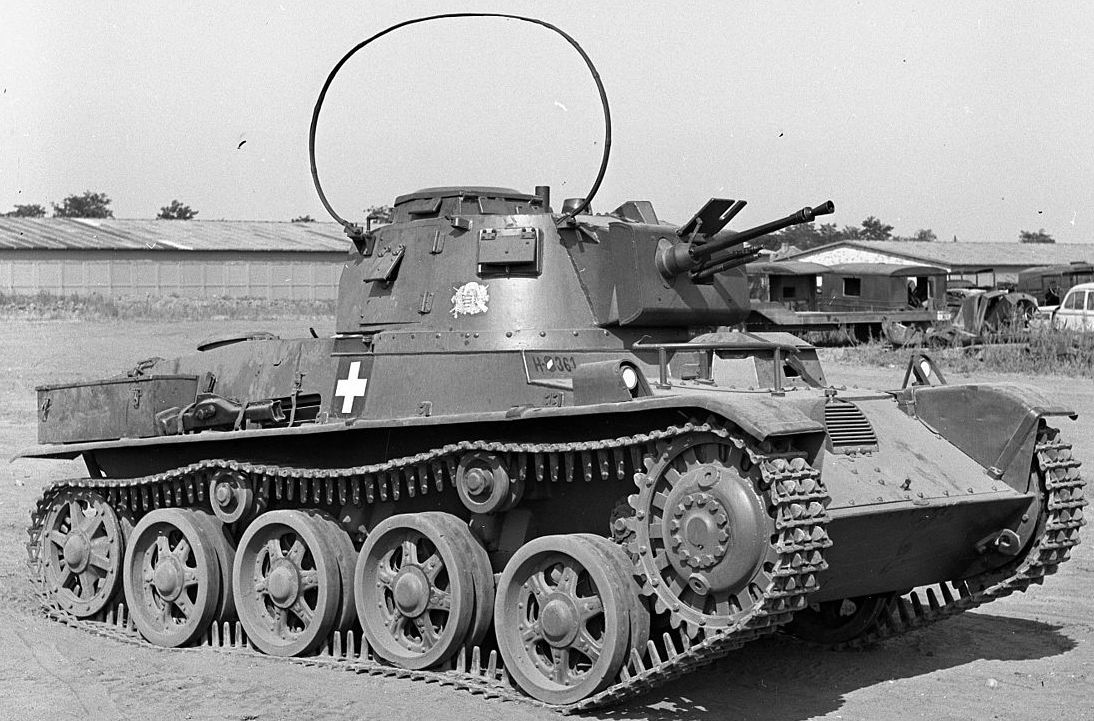


- 12/12/16 mm
- 27/38/10 mm
- 10 rounds
- 12/12 mm
- 35/50 mm
- 10 rounds
- 20/20 mm
- 46/65 mm
- 13/13/6 mm
- 13/13/6 mm
- 155 hp

As mentioned before, in 1938 there was a contest for the Hungarian mass-produce light tank between V-4, Pz. I and L-60. L-60 was far better than other variants, as one imported vehicle showed. This way L-60 got a new armament and was named as Toldi I (It was named after Miklos Toldi, legendary 14th century Hungarian warrior and hero, known for his strength). It was decided to mass-produce this vehicle in Hungary, but mass-production was delayed by squabbles between the producers (MÁVAG and Ganz Gepgyár) and the army over the price. At first, the army wanted to order 64 vehicles, but it was decided at least 80 were needed and the order for 80 tanks was finalized on 17.2.1939.
First two Toldi tanks were finished by February 1940, but the rest were still waiting in the plants for the components. Until June 1940, 20 vehicles in total were completed – by that point the timetable for the entire project was completely off, all 80 vehicles were supposed to be delivered by Spring 1940, but the latest estimates did postpone the production completion to March 1941.


- 12/12/16 mm
- 27/38/10 mm
- 10 rounds
- 12/12 mm
- 35/50 mm
- 10 rounds
- 20/20 mm
- 46/65 mm
- 45/45/60 HP
- 64/80/20 mm
- 13/13/6 mm
- 13/13/6 mm
- 155 hp
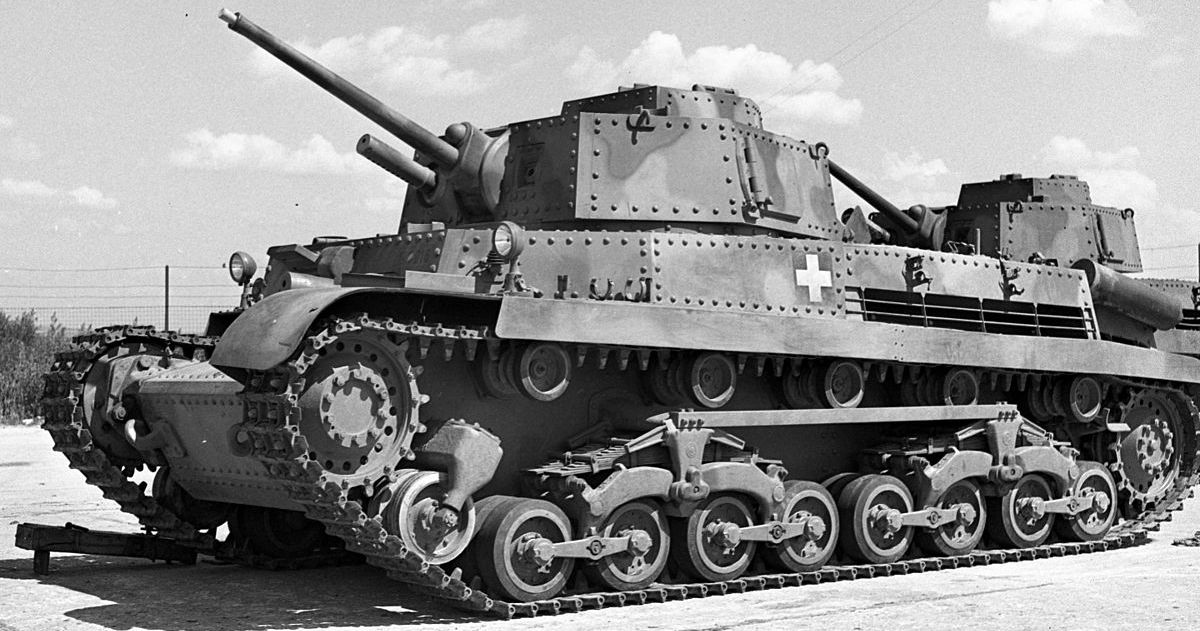


Originally, Toldi II was a name for the next part of produced Toldi I's, so they didn't have much difference. But Toldi IIA is a further development and rearming of the existing Toldi II light tanks. The frontal armor was thickened and the 20mm heavy machine gun was replaced with a 40mm tank gun. Because of their relatively weak and fragile torsion bars, the Toldi I tanks could not be upgraded. In total, 80 38M. Toldi II (Toldi B20) were upgraded to 38M. Toldi IIA (Toldi B40) between 1943-44.

- 50/50/60 HP
- 63/101/23 mm
- 4 rounds
- 13/10/10 mm
- 155 hp
- 155 hp
Self-propelled anti-air and anti-tank autocannon, based on the Swedish Landsverk L-62. In total, 135 36/40M. Nimród vehicles were manufactured between 1940-1941 by the MÁVAG factory. At the early stage of the Second World War, these vehicles were used in anti-tank role as well, not just as mobile anti-air support units. However, after 1942, because of their insufficient firepower against the newer Soviet medium tanks, the Nimróds were moved from the Armored Corps to the Anti-Air Battalion and rarely fought against ground targets from that point onward.


- 110/110/175 HP
- 98/126/38 mm
- 155 hp

In August 1943, the Ganz factory assembled this tank destroyer on the chassis of a Toldi I light tank, based on the experiments with German Marder II. Only one prototype was made and the design never entered mass production.
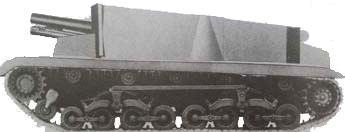
- 350/350/400 HP
- 66/110/53 mm
- 260 hp
Originally this is an early stage of Zrinyi assault gun - with 105 mm howitzer and open top (which was the reason of cancelling of the project) based on Turan tank, which was lately transformed into Zrinyi II itself.
But the problem is nowadays it's known that is the image for VOSS II (Czechoslovak project). I suppose Turan MAVAG looks something like this too, but surely it may differ.


- 45/45/60 HP
- 64/80/20 mm
- 50/50/60 HP
- 80/120/20 mm
- 110/110/175 HP
- 50/101/38 mm
- 50/25/25 mm
- 50/25/25 mm
- 240 hp
- 260 hp
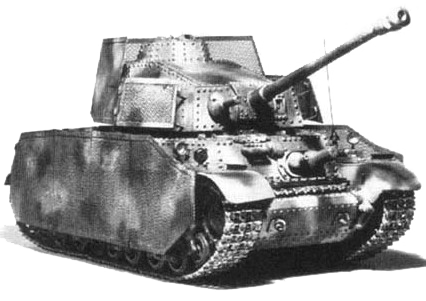
In 1940 the Hungarian Ministry of Defence decided to buy the licence of the yet unfinished design of the Czechoslovak T-21 medium tank, to solve the problem of the missing medium tank class in Hungarian service as soon as possible. However, because the prototype needed plenty of modifications and suffered from many breakdowns during its development, the first 40M. Turán I medium tanks only arrived to the troops in the Summer of 1942. Soon after that, the need for a higher caliber gun arose, so between 1942-1943, the Turán was further developed to 41M. Turán II and recieved a short 75mm cannon in a modified turret. Approximately 459-462 Turán I and Turán II were manufactured during the war.


- 110/110/175 HP
- 113/160/38 mm
- 75/35/55 mm
- 75/35/55 mm
- 260 hp
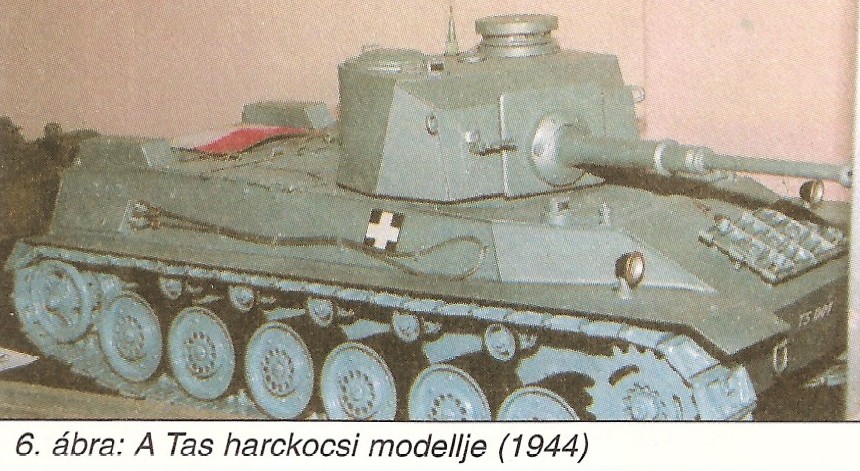

Planned (in 1943) upgrade to put a long 75mm gun on the Turán medium tank. The mass-production never started, because of the late war limited resources and slow development of the desired gun. Only one complete prototype was made.


- 350/410 HP
- 100/50 mm
- 110/110/175 HP
- 113/160/38 mm
- 110/110/175 HP
- 140/180/38 mm
- 260 hp
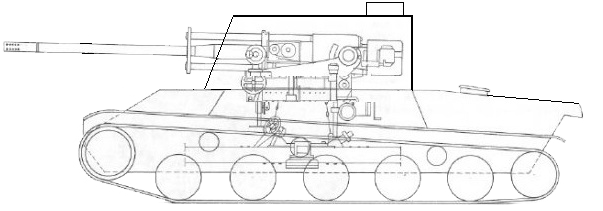
The 40/43M. Zrínyi II assault howitzer entered service in 1943 and became one of the most successful Hungarian armor designs during the World War II. Approximately 71 Zrínyi IIs were manufactured. Along with the assault howitzer, an anti-tank assault gun version was designed as well. The original plan was to build the Zrínyi I and II in 2:1 ratio, but because of the slow development of the required 75mm gun, only one prototype 44M. Zrínyi I assault gun was made before the end of the war.


- 200/200/250 HP
- 120/170/41 mm
- 210/210/260 HP
- 140/200/41 mm
- 200/200/250 HP
- 180/230/41 mm
- 155 hp
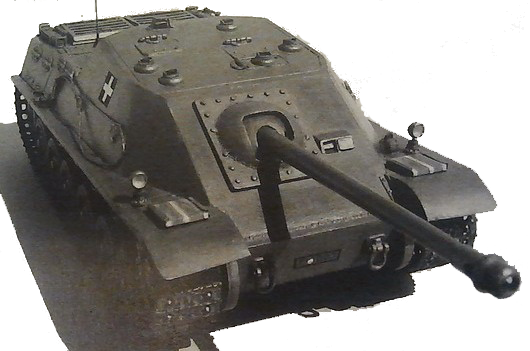
Proposed tank destroyer by György Szebeny, a Hungarian inventor. The main plan was to put an 8cm cannon on a turretless, modified chassis of the 36/40M. Nimród to create an easy to manufacture tank destroyer. The development took place between 1941-1942 and underwent many changes. In the end, the project was halted, because it was considered too expensive and the preparation for the mass production would have been take too much time. No prototype was made, and the idea never left the drawing board.


- 110/110/175 HP
- 113/160/38 mm
- 135/135/175 HP
- 150/194/38 mm
- 100/100/100 mm
- 500 hp
- 520 hp
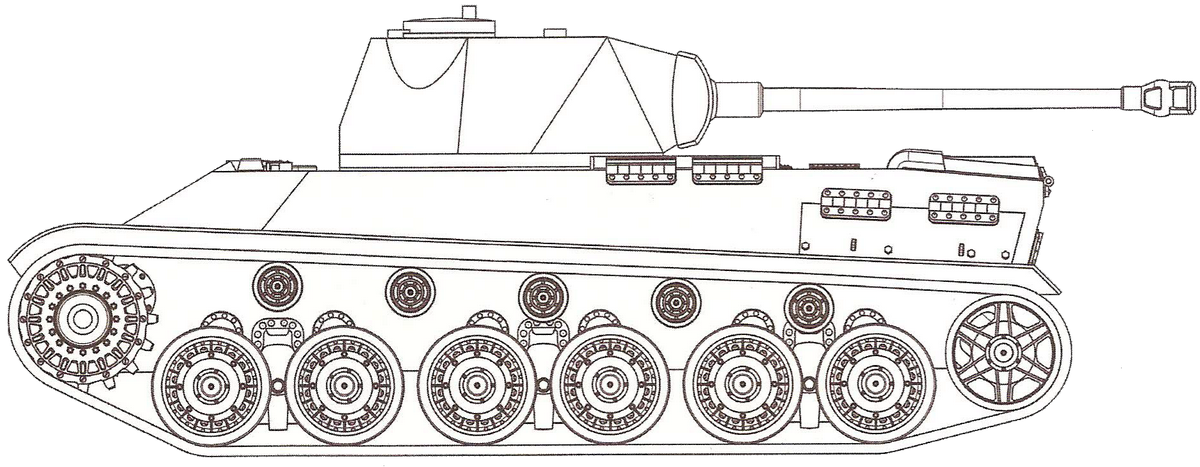
The developoment of this medium/heavy tank started in the Spring of 1943 as an answer to the appearance of the Soviet T-34. The assembly of the first two prototypes was already started in May 1944, but on 27th of June, the Weiss Manfréd factory was seriously hit by an Allied bombing run and the two prototypes were destroyed along with the assembly hall. Shortly after that, the whole development was cancelled.
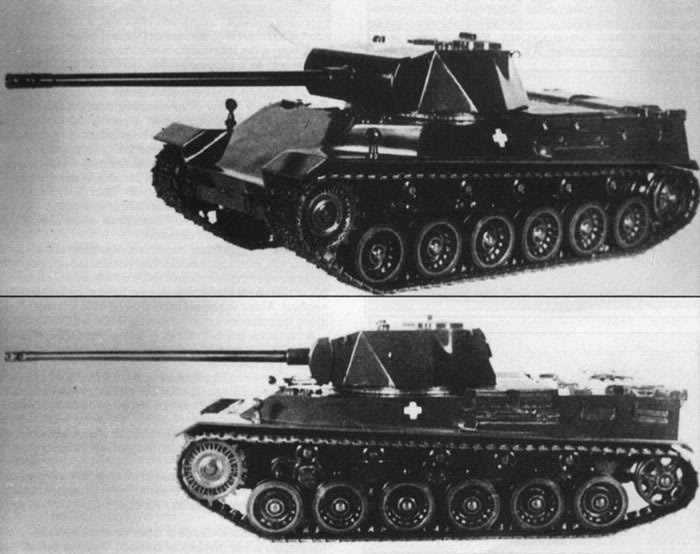

- 110/110/175 HP
- 113/160/38 mm
- 135/135/175 HP
- 150/194/38 mm
- 200/200/250 HP
- 205/255/41 mm
- 100/100/100 mm
- 100/100/100 mm
- 520 hp
- 690 hp
- 700 hp
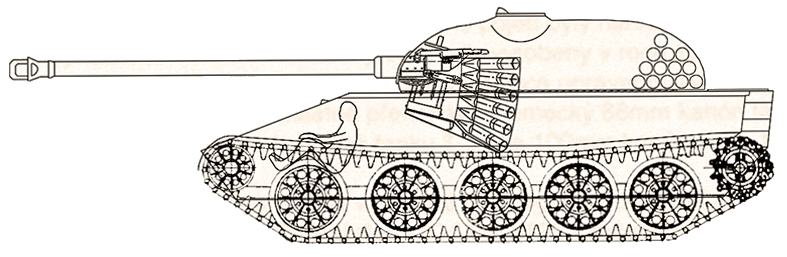
The final, mass-produced version of the Tas. Its development was never completed because of the destruction of the prototypes and WM assembly hall in July 1944 and the late war lack of raw materials and production capacity. Only existed on blueprints.
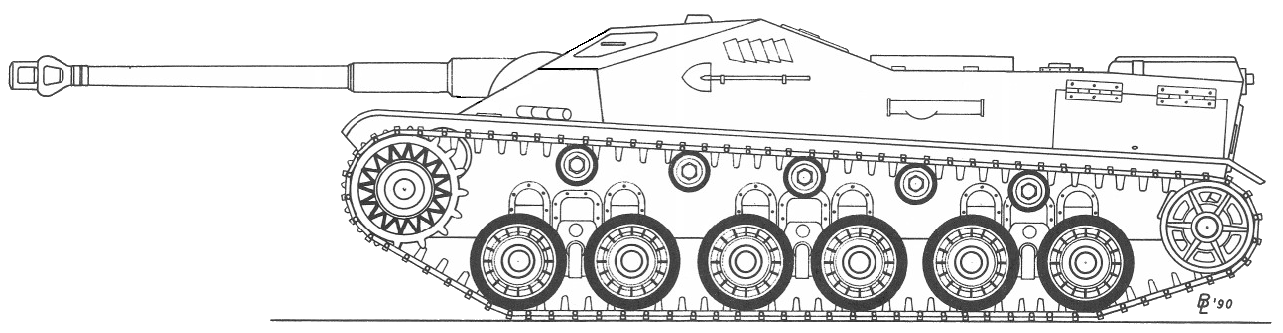

- 110/110/175 HP
- 113/160/38 mm
- 135/135/175 HP
- 150/194/38 mm
- 240/240/295 HP
- 203/237/44 mm
- 200/200/250 HP
- 205/255/41 mm
- 520 hp
- 690 hp
- 700 hp
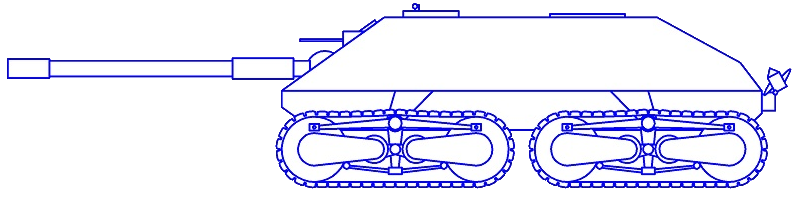
Considered assault gun version of the 44M. Tas. However, the development was never started, and no prototypes were made.
Maybe you've heard some info that a hull for the Rohamloveg was about to be built, but the thing is this info is totally false. The thuthful stage of Tas Rohamloveg is that it barely even was a project - actually, there are no known, official document ever mentions that this assault gun ever existed, except some shady statements and memories.
In 2009, Ádám Bíró, acknowledged Hungarian historian and model-maker wrote a long article about how could(!) have the Tas rohamlöveg looked like, based on his mock-up experiments. However, any of the existing mock-ups or models could not be considered 100% historically correct right now. So here is a picture of his model.



- 250/250/330 HP
- 175/235/50 mm
- 200/160/65 mm
- 200/160/65 mm
- 520 hp

During the Hungarian Revolution in 1956 Soviet troops were introduced to stop it. They used some tanks such as T-54 (especially it's known about the T-54-3 and T-54A), IS-3, T-34-85 ect. Hungarian Republic was fighting to stop revolters as well. These tanks weren't actually a part of the Hungarian Army, but can be used in-game (still better than the Chinese Type T-34).


- 250/250/330 HP
- 175/235/50 mm
- 320/320/420 HP
- 201/330/50 mm
- 200/160/65 mm
- 200/160/65 mm
- 520 hp
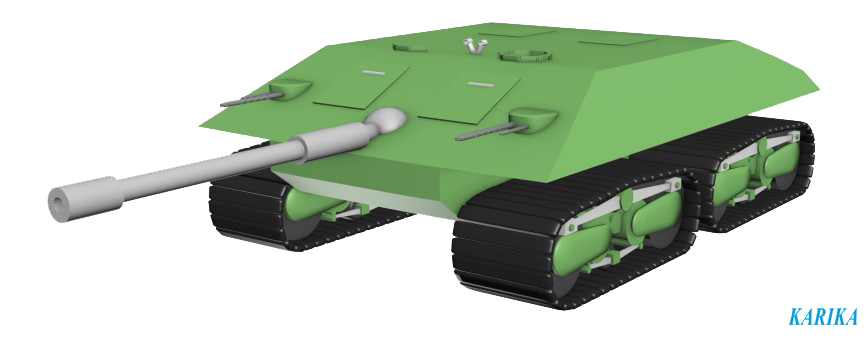
During the Hungarian Revolution in 1956 Soviet troops were introduced to stop it. They used some tanks such as T-54 (especially it's known about the T-54-3 and T-54A), IS-3, T-34-85 ect. Hungarian Republic was fighting to stop revolters as well. These tanks weren't actually a part of the Hungarian Army, but can be used in-game (still better than the Chinese Type T-34).

- 400/400/515 HP
- 259/326/120 mm
- 6 rounds
- 750 hp
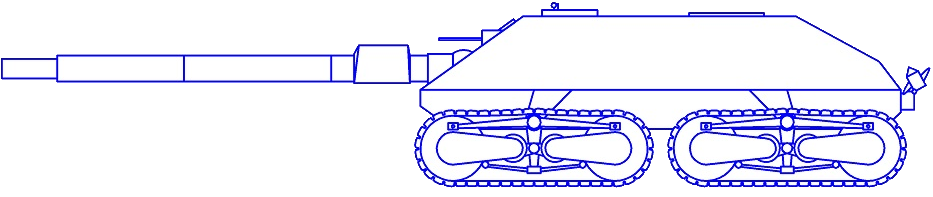
Straussler Main Battle Tank or Straussler MBT was designed sometime between 1959-1961. This idea of „the ideal tank” was presented to the leaders of the British Army in 1961, but they were not interested in this rather unconventional and unproven design, and insisted on continuing the existing next generation tank project, which later became the Chieftain main battle tank.
The tank could drive without tracks using its wheels. It could be implented in the game as there is physics for wheeled vehicles.